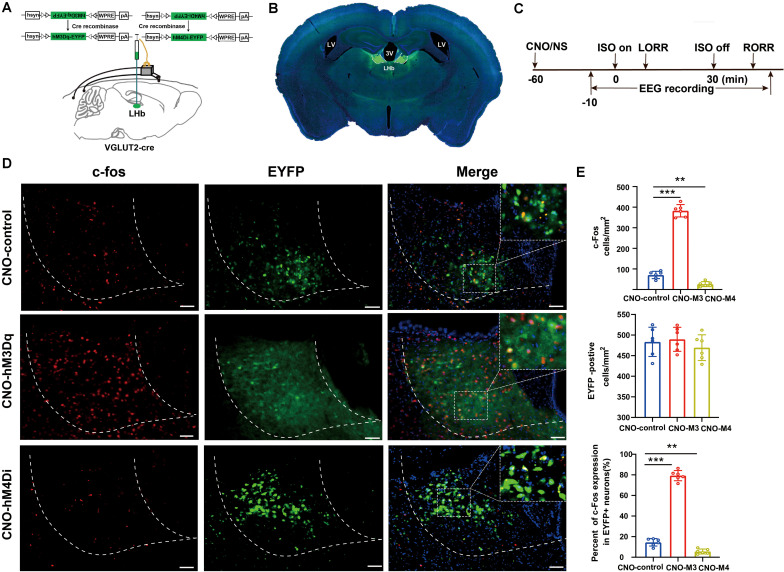
FIGURE 3.
Activation/inactivation of LHb glutamatergic neurons induced LHb c-Fos expression during isoflurane anesthesia. (A) Surgical manipulations and experimental schematic for chemogenetic stimulation of LHb glutamatergic neurons. (B) Representative images of chemogenetic virus expression in LHb (scale bar, 1 mm). (C) Timelines of isoflurane anesthesia-related behavioral and EEG tests measuring induction time (LORR) and emergence time (RORR). (D) Representative images of c-Fos expression (red) and EYFP (green) in control (EYFP), hM3Dq-CNO and hM4Di-CNO mice groups after treatment with CNO (scale bar, 100 μm). (E) CNO administration decreased c-Fos expression in mCherry + neurons by 74%. Quantification of CNO administration induced the number of c-fos-positive neurons, the number of EYFP-positive neurons, and the percent of c-Fos expressing in EYFP-positive neurons after CNO administration (CNO administration significantly increased c-Fos expression in EYFP + neurons, P < 0.001 by Bonferroni’s post hoc test after one-way ANOVA; CNO administration decreased c-Fos expression in EYFP + neurons, P = 0.002 by Bonferroni’s post hoc test after one-way ANOVA; n = 6 per group; mean ± SD; **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001).