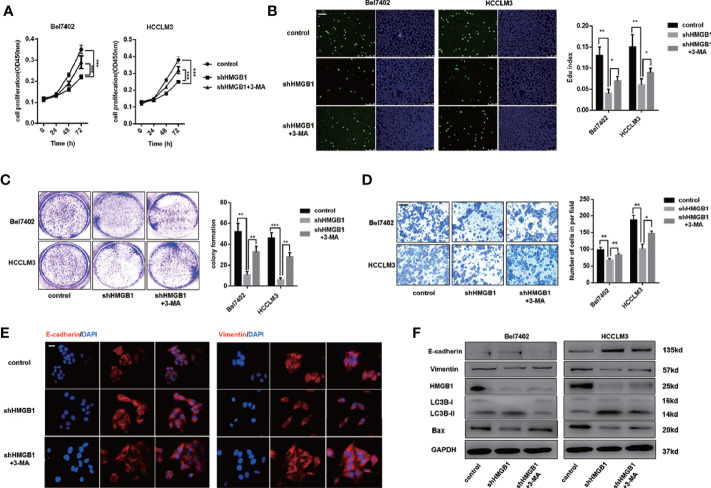
Figure 3.
HMGB1 deficiency inhibits HCC development via autophagy induction. (A) Cell proliferation of HCC cells transfected as described, was determined by CCK-8 assays. 3-MA treatment (5mM) partly recovered damaged proliferation capacity of shHMGB1 cells. (B) Representative images of HCC cells stained by Edu assays. Numbers of Edu positive cells were counted and analyzed. 3-MA treatment (5 mM) partly recovered damaged Edu index of shHMGB1 cells. Scale is 400 μm. (C) Experiments of colony formation were performed in 12-well plates and results were analyzed. (D) Invasive capacity of HCC cells were determined by transwell experiments. Numbers of invaded cells were counted and analyzed. 3-MA treatment (5 mM) partly recovered impaired invasive capacity of shHMGB1 cells. Scale is 100 μm. (E) Representative images of IF staining E-cadherin and Vimentin in HCC cells with varied treatments, scale is 100 μm. (F) Immunoblot analysis of E-cadherin, Vimentin, BAX and autophagy markers was performed. 3-MA treatment (5 mM) partly recovered impaired EMT phenotype and BAX expression of shHMGB1 cells. Data are means ± SEM from three independent experiments, * means p<0.05, ** means p<0.01, *** means p<0.001 by unpaired student T test.