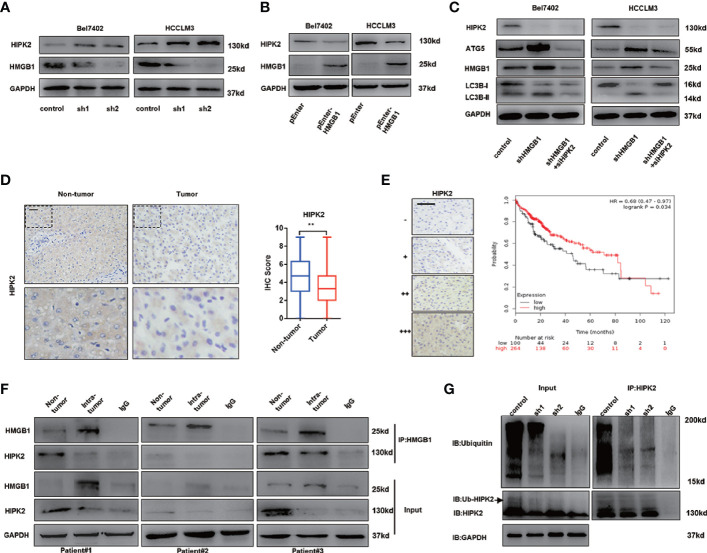
Figure 4.
HMGB1 promotes the protein stability of HIPK2. (A) Protein levels of HIPK2 were determined in two HCC cell lines with a non-targeting control lentivirus-shRNA (control) or two lentivirus-shRNA targeting HMGB1 mRNA (sh1, sh2). (B) Protein levels of HIPK2 were determined in two HCC cell lines transfection with plasmid control (control) or plasmid HMGB1 (pEnter-HMGB1, 2μg/ml). (C) Identification of the essential role of HIPK2 in autophagy induction in both Bel7402 shHMGB1 and HCCLM3 shHMGB1 HCC cells by HIPK2 siRNA transfection in (siHIPK2). (D) Representative images of IHC staining HIPK2 in non-HCC and HCC tissue, scale is 100 μm. Quantification of HIPK2 levels according to IHC scores in non-tumor and tumor tissue. (E) Representative images of HIPK2 levels in HCC tissues, scale is 100 μm. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis of HCC patients based on HIPK2 levels by using public data (http://kmplot.com/analysis/index.php?p=service&cancer=liver_rnaseq). (F) Identification of the HMGB1-HIPK2 interaction in non-HCC and HCC tissue from three patients by co-immunoprecipitation. Endogenous HIPK2 was pulled down with anti-HMGB1, compared with IgG, and vice versa and detected by immunoblotting. (G) Immunoprecipitation of HIPK2 was performed with lysates of Bel7402 cells treated by a non-targeting control lentivirus-shRNA (control) or two lentivirus-shRNA targeting HMGB1 mRNA (sh1, sh2). Ubiquitination of precipitated HIPK2 was determined by Western blotting. Data are means ± SEM from three independent experiments, * means p<0.05, ** means p<0.01, *** means p<0.001 by unpaired student T test.