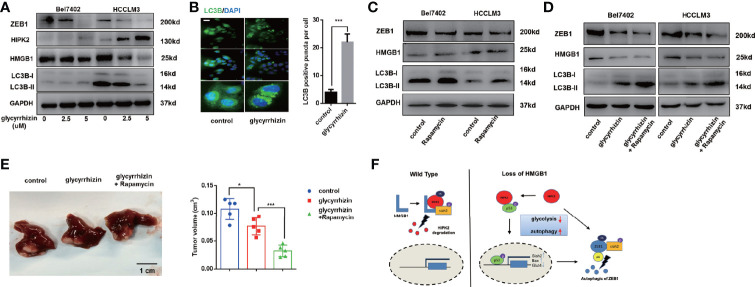
Figure 8.
HMGB1 inhibitor exerts more efficient anti-HCC effects in combination with Rapamycin. (A) Related protein levels were determined in HCC cells treated with HMGB1 inhibitor glycyrrhizin (2.5 mM). (B) Representative images of IF staining LC3B in Bel7402 cells treated with or without glycyrrhizin (2.5 mM). Scale is 100 μm. (C) Related protein levels were determined in HCC cells treated with autophagy inducer Rapamycin (100 nM). (D) Rapamycin treatment enhanced the anti-HCC effects of glycyrrhizin. (E) Identification the inhibiting role of glycyrrhizin (50 mg/kg, i.p., twice every week for 4 weeks) with or without Rapamycin (10 mg/kg, i.p., twice every week for 4 weeks) in vivo. n=5. (F) Schematic depicting the role of HMGB1 in the regulation of HCC progression.