TABLE 7.
he other.
| Natural drugs | Compounds | Chemical structure | Animal models | Mechanisms | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Curcuma longa L. (turmeric) | Curcumin |
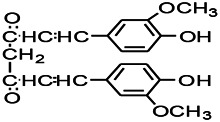
|
PTZS and KAS in mice | Inhibit MTORc1 activation; Reduce the damage of hippocampal neurons and cognitive dysfunction | Kiasalari et al. (2013) |
| Citrus aurantium L. (Rutaceae) | Naringin |
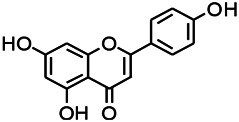
|
KAS in mice | Reducing GCD and mtorc1 activation | Diniz et al. (2015) |
| Sophora japonica L. (Fabaceae) | Rutin |
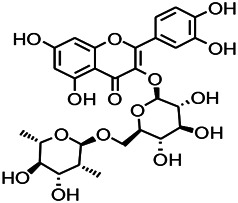
|
PTZS in zebrafish; KAS in mice | Improving epileptoid action | Diniz et al. (2015) |
| Folium Sennae (Senna) | Vitexin |
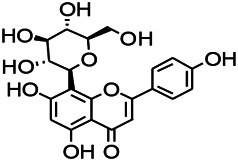
|
PTZ-CS | Neuroprotective effects | Diniz et al. (2015) |
| Achillea millefolium L. (Yarrow) | Kaempferol |
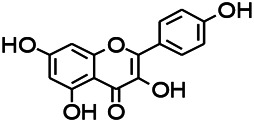
|
Epileptic drosophila | Inhibition of DNA topoisomerase I enzyme | Diniz et al. (2015) |
| Smoke tree (Cotinus coggygria) | Fisetin |
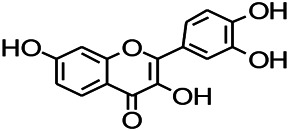
|
Iron-induced experimental model in rats | Protecting endogenous enzyme level | Diniz et al. (2015) |
| Dendranthema morifolium (Ramat.) Tzvelev | Linarin |
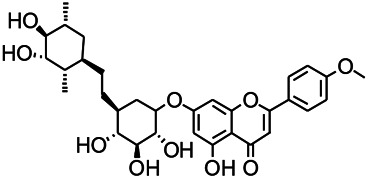
|
PTZS in mice | Preventing CNS excitation or stress | Diniz et al. (2015) |
| Cannabis sativa L. (Moraceae, hemp) | Cannabidiol |
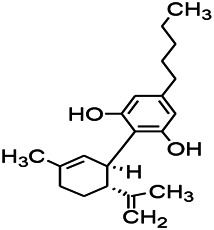
|
Patients | Inhabiting neuronal excitability | Xiang et al. (2014) |
| Herba Menthae Haplocalycis (Mentha haplocalyx Briq.) | Carvone |
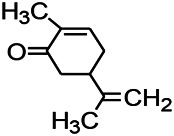
|
PTZS in mice | Inhibiting central nervous system | Xiang et al. (2014) |
| Origanum vulgare L. (Lamiaceae Martinov) | Γ-terpinene |
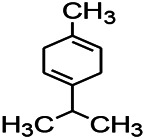
|
PTZS, MES in mice | Raising the threshold of convulsion | Xiang et al. (2014) |
| Norway spruce (Picea abies (L.) Karst.) trees | Verbenone |
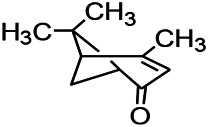
|
PTZS in mice | Related to RNA expression of COX-2, BDNF, and C-fos | Bahr et al. (2019) |
| Cannabis sativa (marihuana) | Delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol |
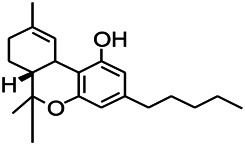
|
PTZS in mice | Improving seizures in children | Bahr et al. (2019) |
| Nepeta cataria L. var. citriodora (Lamiaceae) | Ursolic acid |
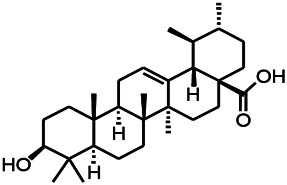
|
PTZS in mice | Unknown | Nieoczym et al. (2018) |
| Moschus moschiferus L | Muscone |
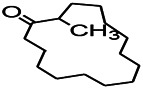
|
Rat | Inhibiting the central nervous system excitability | Bahr et al. (2019) |
| The fragrant camphor tree (Cinnamomum camphora) | Borneol |
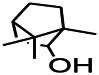
|
PTZS in mice | Anti-bacterial; protecting central nervous | Tambe et al. (2016) |
| Aconitum carmichaeli Debx. (Ranunculaceae) | Mesaconitine |
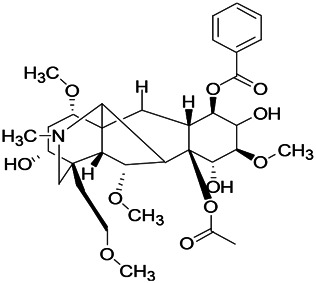
|
Wistar rats | Regulating the noradrenergic system | Zhao et al. (2020) |
| Rhizoma Corydalis (Papaveraceae) | Dl-Tetrahydropalmatine |
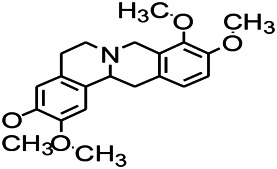
|
Electrical kindling in rats | Reducing dopamine output | Lin et al. (2002) |
| Rauwolfia serpentine (Sarpagandha) | Raubasine |
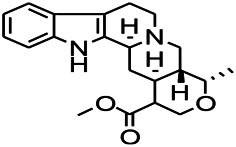
|
PTZS in mice | Interacting at benzodiazepine sites with a benzodiazepine agonist-type activity | Xiang et al. (2014) |
| Piper nigrum L. (Pepper berries) | Piperlongumine |
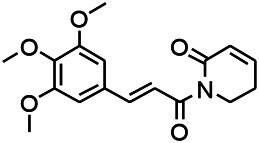
|
PTZS in mice | Decreasing the latency to death in mice | Xiang et al. (2014) |
| Erythrina mulungu Mart ex Benth (Papilionaceae) | Erythravine |
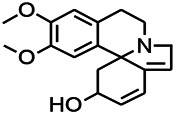
|
BCLS in Wistar rats | Unclear | Xiang et al. (2014) |
| Ligusticum chuanxiong hort (Umbelliferae) | Tetramethylpyrazine |
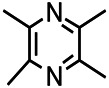
|
Epileptic Sprague Dawley rats | Increasing neuron cell adhesion molecule -140 | Jin et al. (2019) |
| Peucedanum praeruptorum dunn (Umbelliferae) | Imperatorin |
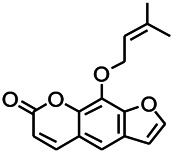
|
MES in mice | Upregulating of BDNF levels | Chowdhury et al. (2018) |
| Heracleum mantegazzianum s.l. (Giant hogweed) | Umbelliferone |

|
MES in mice | Unclear | Zagaja et al. (2015) |
| Zanthoxylum schinifolium Sieb. et Zucc. (Rutaceae) | Xanthotoxin |
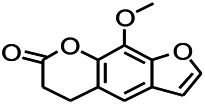
|
MES in mice | Unclear | Zagaja et al. (2016) |
| Acorus tatarinowii Schott (Araceae) | α-asarum |
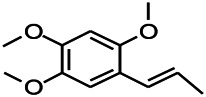
|
Caco -2 cells | Decreased expression of P glycoprotein and multidrug resistance gene | Yuan and Liu. (2020) |
BCLS, bicuculline induced seizure; KAS, Kainic acid (KA)-induced seizures; MES, Maximal electroshock-induced seizures; PTZS, PTZ-induced seizures; PTZ-CS, PTZ induced chronic seizures.
