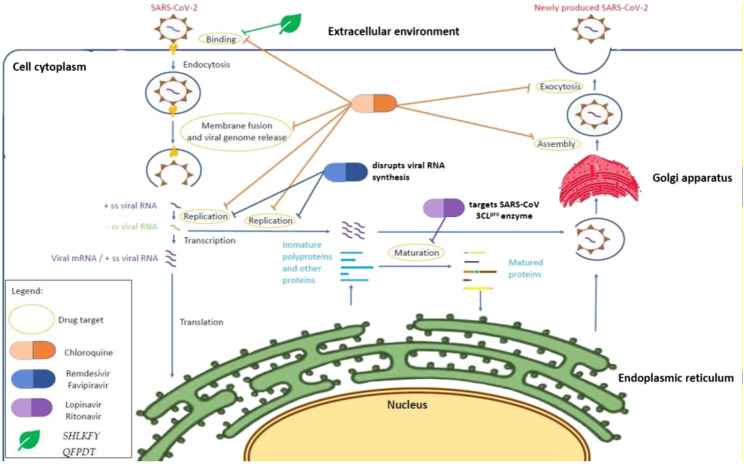
FIGURE 2.
Mechanism of action of repurposing drugs against SARS-CoV-2 within a host cell. Chloroquine inhibits SARS-CoV-2 at the cellular level (Wang M. et al., 2020) when the pH environment is disrupted. HIV protease inhibitors such as lopinavir and ritonavir may demonstrate an antiviral effect through binding to the SARS-CoV 3CLpro enzyme (Nukoolkarn et al., 2008), whereas nucleotides analogues (remdesivir and favipiravir) disrupt the viral RNA synthesis through chain termination (Sangawa et al., 2013; Abdelnabi et al., 2017). On the other hand, Shuang Huang Lian Kou Fu Ye and Qing Fei Pai Du Tang are suspected to inhibit the binding on angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE2) owing to the presence of baicalin from Scutellaria baicalensis (Yang et al., 2020). The action of oseltamivir and the other two alternative and complementary medicines (Combination of Bu Huan Jin Zheng Qi San and Da Yuan Yin and Xue Bi Jing Injection) remained unknown and are suspected to inhibit the viral neuraminidase according to their previous antiviral effect in influenza virus particles (Mulangu et al., 2019; Harrison, 2020) and altering of the TLR7 signaling pathway (Cheng et al., 2016).