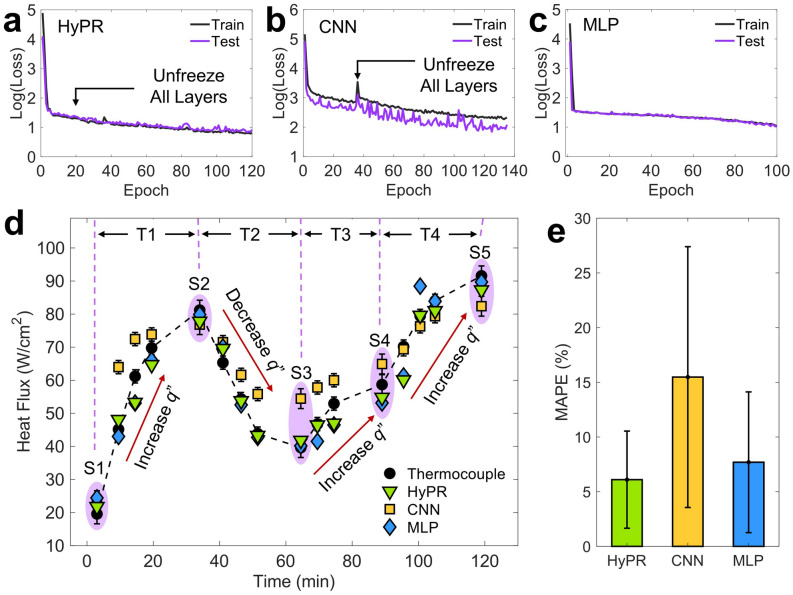
Figure 5.
Real-time prediction of boiling heat flux using trained deep learning models. The training results for the (a) HyPR, (b) CNN, and (c) MLP models show all three models can learn well from the teaching dataset with a testing loss of 2.49, 7.11, and 5.36, respectively. The losses are plotted in log scales to show the exponential decay. (d) The trained models predict real-time steady state (S1-5) and transient state (T1-4) heat fluxes. The HyPR and MLP models respond well to the increasing and decreasing boiling curves, demonstrating minimal deviations. In contrast, the CNN models follow the general trend of the varying heat flux; however, overpredicts mid-range heat fluxes from 40 to 60 W/cmy. Error bars represent the standard deviation of the predictions of all 500 images for each heat flux step. (e) Mean absolute percentage errors (MAPE) characterize the realistic prediction accuracy, where the HyPR, CNN, and MLP models report 6%, 15%, and 8% mean error, respectively. The error bars show the standard deviation of MAPE.