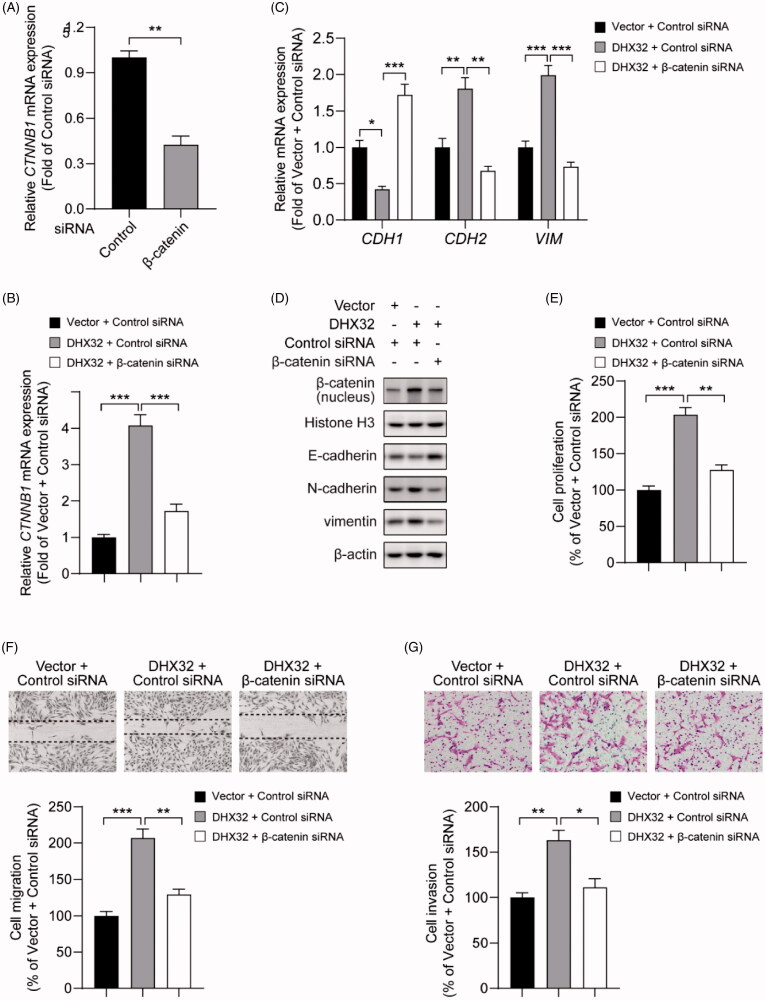
Figure 5.
Silencing β-catenin inhibits DHX32-induced HCC progression. (A) RT-PCR assay for the expression of β-catenin (CTNNB1) mRNA in Huh7 cells. (B) RT-PCR assay was used to detect the expression of β-catenin (CTNNB1) mRNA in Huh7 cells after co-transfection with DHX32 and β-catenin siRNA. (C)Representative blot of the expression of β-catenin in nucleus, E-cadherin, N-cadherin, and vimentin in Huh7 cells with DHX32 overexpression plus β-catenin knockdown. (D) RT-PCR assays were performed to determine the expression of E-cadherin, N-cadherin, and vimentin in Huh7 cells. (E) Quantification of the number of EdU-positive Huh7 cells. (F) Wound-healing assay was used to detect the effect of silencing β-catenin on migration in DHX32-overexpressing HCC cells. Representative images and quantification of cell migration are shown. Magnification, 200 ×. (G) Representative images and quantification of the invaded Huh7 cells after co-transfected with DHX32 lentiviral particle and β-catenin siRNA. Data are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 5). *p < .05, **p < .01, and ***p < .001.