Figure 9.
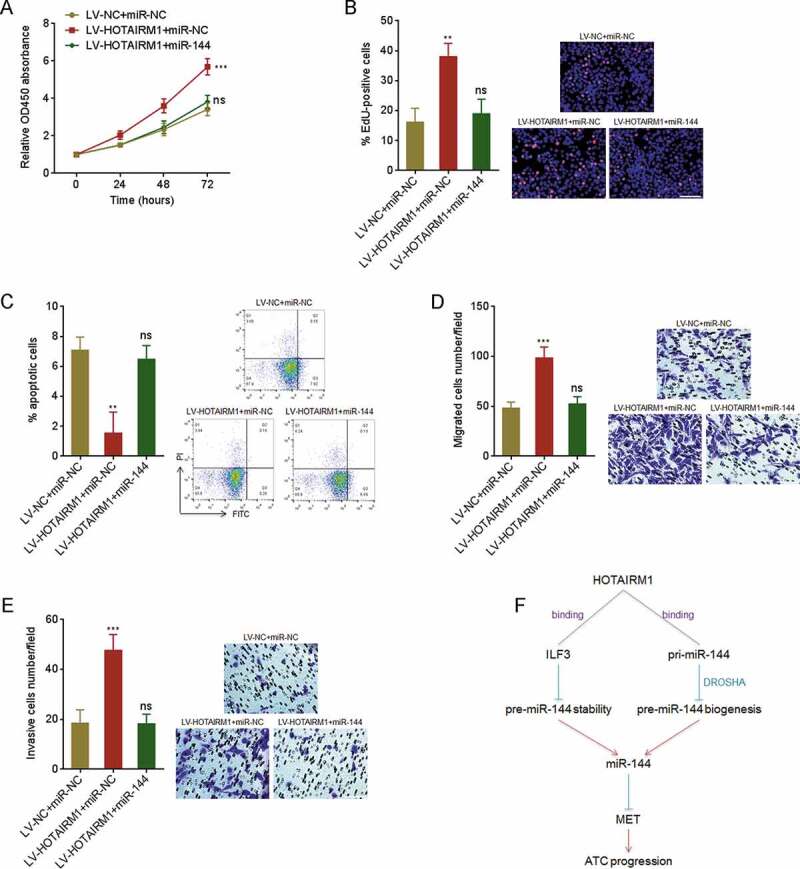
The roles of HOTAIRM1 in proliferation, apoptosis, migration and invasion of ATC cells are dependent on the inhibition of miR-144. (A) After transient transfection of miR-144 mimics or miRNAs negative control (miR-NC) into HOTAIRM1 overexpressed or control 8505 C cells, cell proliferation was measured by CCK-8 assays. Absorbance values at 450 nm were measured to track cell proliferation. (B) After transient transfection of miR-144 mimics or miR-NC into HOTAIRM1 overexpressed or control 8505 C cells, cell proliferation was measured by EdU incorporation assays. Red colour indicates EdU positive and proliferative cells. Scale bar = 100 μm. (C) After transient transfection of miR-144 mimics or miR-NC into HOTAIRM1 overexpressed or control 8505 C cells, cell apoptosis was measured by Annexin-V-FITC/PI staining, followed by flow cytometry. (D) After transient transfection of miR-144 mimics or miR-NC into HOTAIRM1 overexpressed or control 8505 C cells, cell migration was measured by transwell migration assays. Scale bar = 100 μm. (E) After transient transfection of miR-144 mimics or miR-NC into HOTAIRM1 overexpressed or control 8505 C cells, cell invasion was measured by transwell invasion assays. Scale bar = 100 μm. (F) Schematic of the roles of HOTAIRM1 in ATC progression via repressing miR-144. Data were shown as mean ± standard deviation of three independent experiments. ns, not significant, **P < 0.01, ****P < 0.0001 by one-way ANOVA, followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test
