Figure 1.
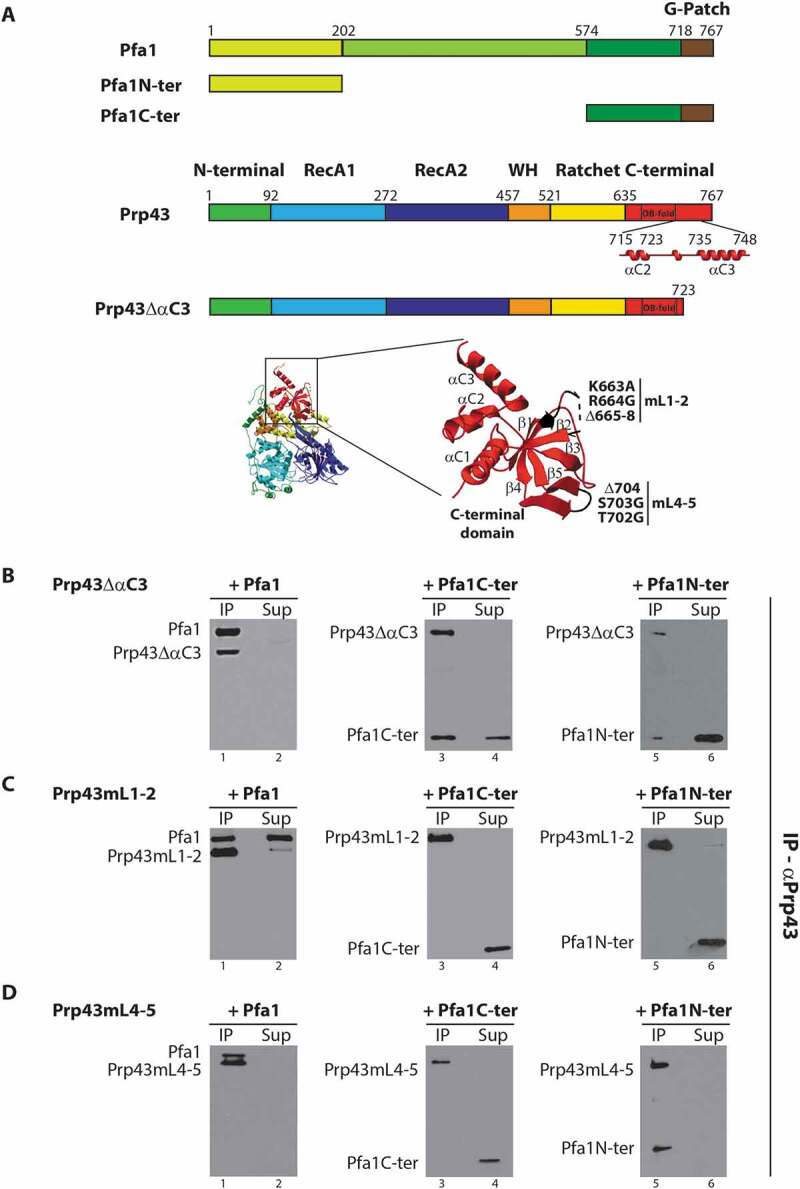
Effects of deletions and/or amino-acid substitutions within Prp43 C-terminal domain on Pfa1C-ter binding. (A) Top: Schematics of Pfa1 and Prp43 domain organization and mutants used in IPs. Bottom: Structure of Prp43 OB fold and terminal alpha helices. Mutations in loops connecting strands β1 and β2 (mL1-2) and strands β4 and β5 (mL4-5) are highlighted. Mutation mL1-2 corresponds to K663A, R664G amino-acid substitutions and deletion of residues 665 to 668. Mutation mL4-5 corresponds to T702G, S703G amino-acid substitutions and deletion of K704. The structure was drawn using the data deposited in the protein data base (PDB) under the code 2xau [17]. (B-D) Purified HIS-tagged mutant versions of Prp43, namely Prp43ΔαC3 (B), Prp43mL1-2 (C) or Prp43mL4-5 (D), were mixed with either purified HIS-tagged Pfa1, Pfa1C-ter or Pfa1N-ter prior to immunoprecipitation using anti-Prp43 antibodies. Proteins from the supernatants were then TCA precipitated. Proteins present in the pellets (lanes IP) and in the supernatants (lanes Sup) were separated by SDS-PAGE, transferred to nitrocellulose membranes and analysed by Western using HRP-coupled anti-histidine antibodies
