Figure 7.
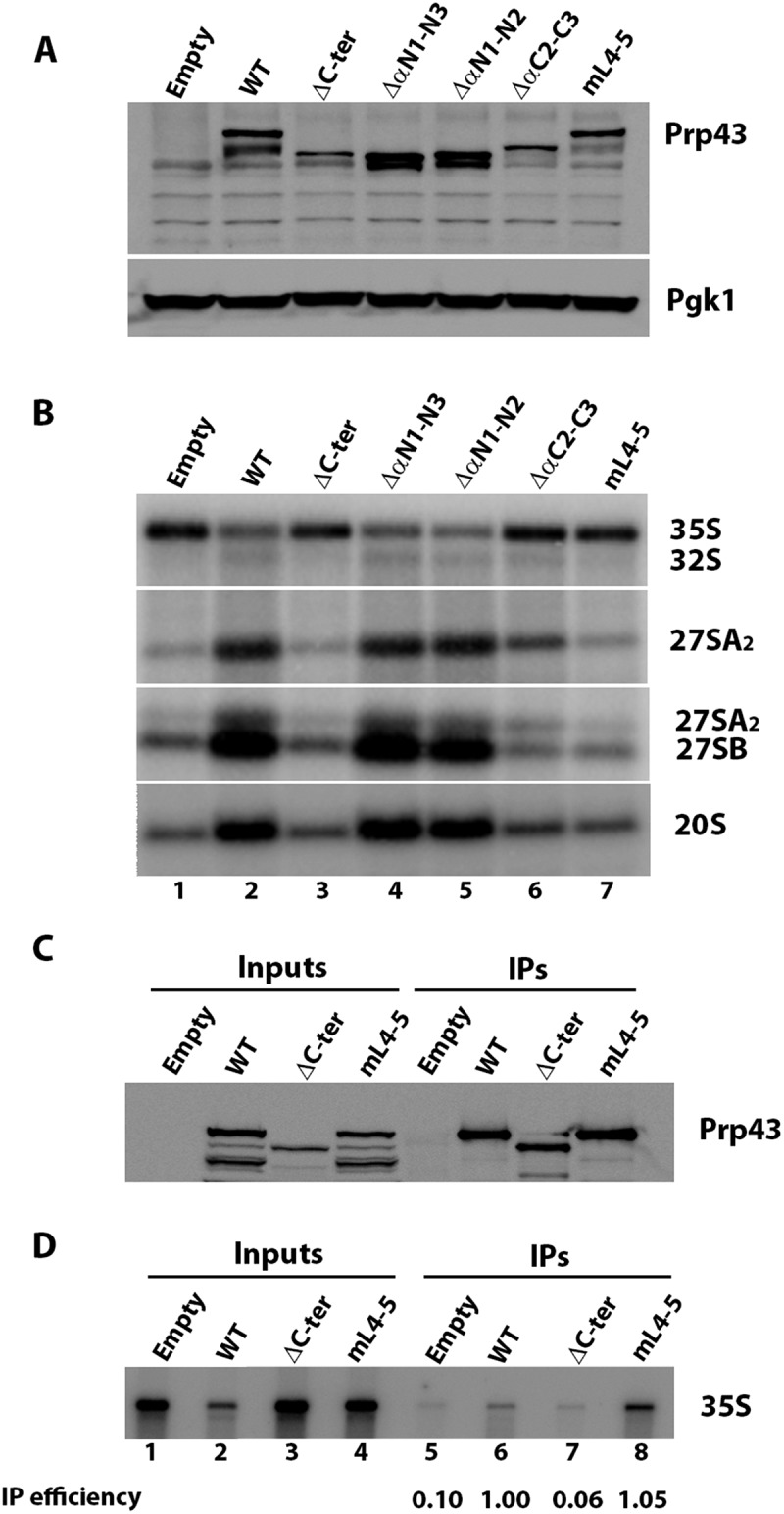
Integrity of Prp43 C-terminal domain is essential for ribosome biogenesis. (A) Western analysis of accumulation of ProtA-tagged wild-type (WT) or Prp43 variants in GAL::prp43 cells grown 13 hours in glucose-containing minimal medium. Empty: cells transformed with empty parental vector. Prp43 proteins were detected using rabbit PAP. Pgk1, detected using specific antibodies, was used as loading control. (B) Northern analysis of pre-rRNA accumulation in GAL::prp43 cells depleted of endogenous Prp43 and expressing ProtA-tagged wild-type (WT) or the indicated Prp43 variants. Names of the various pre-rRNAs detected using anti-sense oligonucleotide probes are indicated on the right. (C) Western analysis of ProtA-tagged wild-type (WT), Prp43ΔC-ter (ΔC-ter) or Prp43mL4-5 (mL4-5) precipitation. Precipitation experiments were carried out with IgG-sepharose and extracts of GAL::prp43 cells transformed with plasmids directing expression of the above-listed proteins or the empty vector and grown 13 hours in glucose-containing minimal medium. Input: aliquots of input extracts; IPs: precipitated samples. Prp43 proteins were detected using rabbit PAP. (D) Corresponding Northern analysis to assess 35S pre-rRNA co-precipitation. The 35S pre-rRNA immunoprecipitation efficiency relative to wild-type (arbitrarily set at 1) assessed by phosphorimager scanning of the Northern blot is indicated below each IP lane
