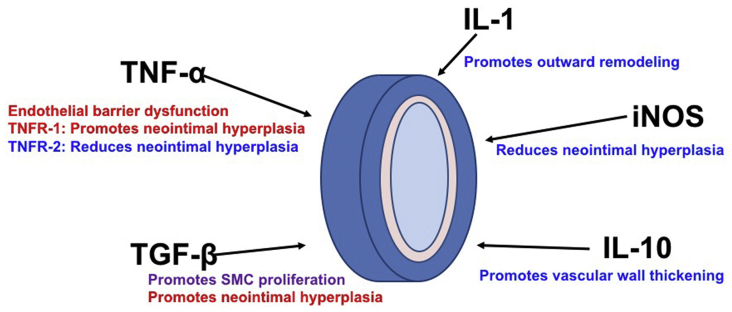
Fig 3.
Associations between effector cytokines and venous remodeling. Tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) causes endothelial barrier dysfunction. Tumor necrosis factor receptor (TNFR)-1 signaling promotes neointimal hyperplasia, but TNFR-2 signaling reduces neointimal hyperplasia. Transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) promotes vascular smooth muscle cell (SMC) proliferation and neointimal hyperplasia. Interleukin (IL)-1 promotes outward remodeling. Inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) decreases neointimal hyperplasia. IL-10 promotes vascular wall thickening. Factors promoting adaptive venous remodeling are shown in blue and factors inhibiting adaptive venous remodeling are shown in red. Factors having both effects on venous remodeling are shown in purple.