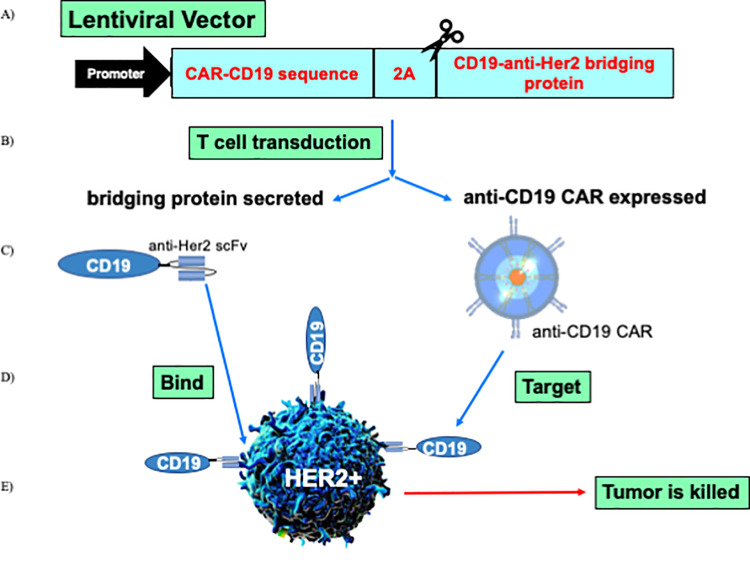
Fig 1. Schematic representation of the technology.
A) A lentiviral expression vector was created that encodes an anti-CD19 CAR domain, a 2A cleavage site, and a secreted CD19-anti-Her2 scFv bridging protein. B) Human primary T cells were transduced and expanded. C) The T cell transduction resulted in the expression of the anti-CD19 CAR domain on the T cell surface (thus, CAR-CD19) and secretion of the bridging protein. D) The bridging protein has two domains: the anti-Her2 scFv bound to Her2 expressed on the tumor cell; the CD19 ECD bound to the anti-CD19 CAR domain on the transduced T cell. Thus the bridging protein acts as a CAR-T cell engager protein. E) The binding events created a cytotoxic immune synapse between the CAR-CD19 T cell and the Her2-positive tumor cell via recognition of CD19; this resulted in CAR T cell proliferation and tumor cell death.