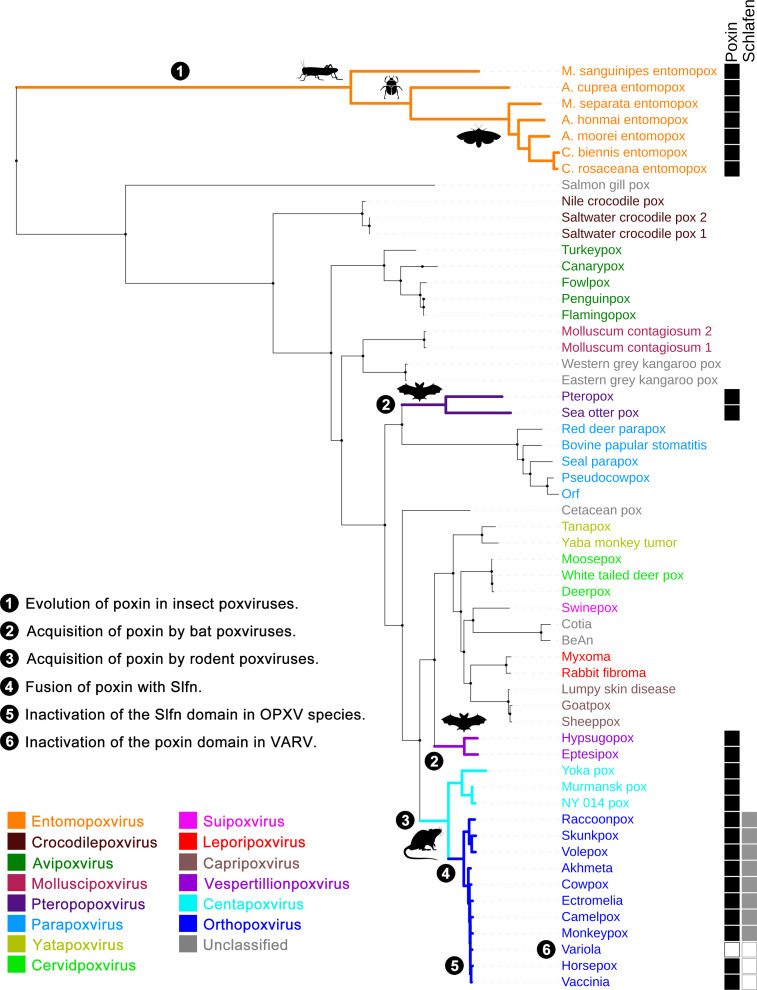
Fig 1. Distribution of cGAMP nucleases across poxvirus species and genera.
A representative maximum-likelihood phylogenetic tree for the Poxviridae family was generated from a multiple sequence alignment of the DNA-dependent RNA polymerase subunit 147 kDa protein (RPO147, J6R) from reference species, colour-coded according to their current classification. Accession numbers were as follows: vaccinia virus, AY243312; horsepox virus, DQ792504; variola virus, X69198; monkeypox virus, AY603973; camelpox virus, AF438165; ectromelia virus, NC_004105; cowpox virus, NC_003663; akhmeta virus, MH607143; volepox virus, KU749311; skunkpox virus, KU749310; raccoonpox virus, KP143769; NY poxvirus, MF001305; Murmansk poxvirus, MF001304; Yoka poxvirus, HQ849551; eptesipox virus, NC_035460; hypsugopox virus, MK860688; sheeppox virus, NC_004002; goatpox virus, AY077835; lumpy skin disease virus, AF409137; rabbit fibroma virus, AF170722; myxoma virus, AF170726; BeAn virus, KY094066; Cotia virus, KM595078; swinepox virus, AF410153; deerpox virus, AY689436; white tailed deer poxvirus, MF966153; moosepox virus, MG751778; Yaba monkey tumor virus, AY386371; tanapox virus, EF420156; cetacean poxvirus, MN653921; orf virus, AY386264; pseudocowpox virus, NC_013804; seal parapox virus, KY382358; bovine papular stomatitis virus, AY386265; red deer parapox virus, KM502564; sea otter poxvirus, MH427217; pteropox virus, KU980965; eastern grey kangaroo poxvirus, MF661791; western grey kangaroo poxvirus, MF467280; molluscum contagiosum virus 1, NC_001731; molluscum contagiosum virus 2, MH320549; flamingopox virus, MF678796; penguinpox virus, KJ859677; fowlpox virus, AF198100; canarypox virus, AY318871; turkeypox virus, KP728110; saltwater crocodile poxvirus 1, MG450915; saltwater crocodile poxvirus 2, MG450916; Nile crocodile poxvirus, DQ356948; salmon gill poxvirus, KT159937; C. rosaceana entomopox virus, HF679133; C. biennis entomopox virus, HF679132; A. moorei entomopox virus, AF250284; A. honmai entomopox virus, HF679131; M. separata entomopox virus, HF679134; A. cuprea entonomopox virus, AP013055; M. sanguinipes entomopox virus, NC_001993. Sequences were manually retrieved and aligned using Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) package. This multiple sequence alignment was used to construct the phylogenetic tree. The presence of poxin in a lineage is indicated by coloured branches and a solid black box on the right-hand side. The presence of a Slfn domain is indicated by a solid grey box next to the poxin box. Empty boxes indicate gene inactivation (defined by the presence of at least one premature STOP codon truncating the predicted open reading frame).