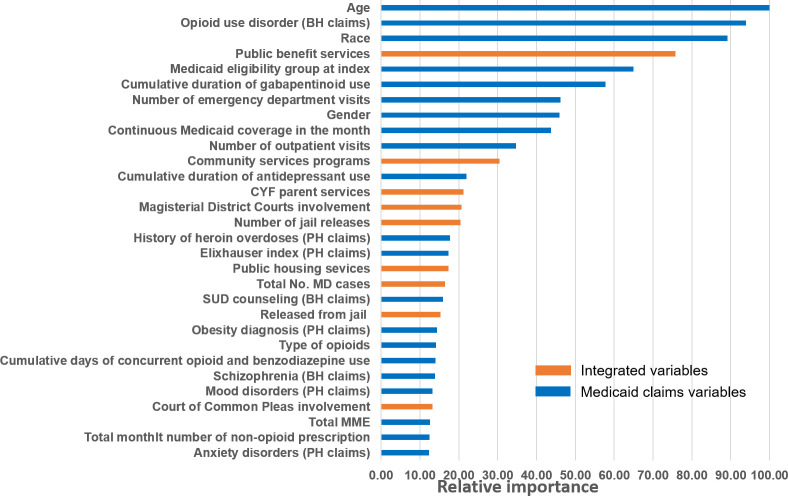
Fig 3. Top 30 predictors for opioid overdose (fatal/nonfatal) identified by gradient boosting machine model integrated with Department of Human Services and criminal justice records data (ordered by importance)a.
a Rather than p values or coefficients, the GBM reports the importance of predictor variables included in a model. Importance is a measure of each variable’s cumulative contribution toward reducing the squared error, or heterogeneity within the subset, after the data set is sequentially split based on that variable. Thus, it reflects a variable’s impact on prediction. Absolute importance is then scaled to give relative importance, with a maximum importance of 100. For example, the top 5 important predictors identified from GBM included age, opioid use disorder diagnosis identified from behavioral health claims, race, public benefit services, and Medicaid eligibility group. *: These variables were binary indicators derived from Allegheny County Data Warehouse that may be captured either from state public services data or Medicaid claims. Abbreviations: BH: Behavioral health; CP: Common Plea Court; CYF: Child, Youth, and Family; DHS: Department of Human Services; GBM: Gradient boosting machine; MD: Magisterial District Court; PH: Physical health; SUD: Substance use disorders.