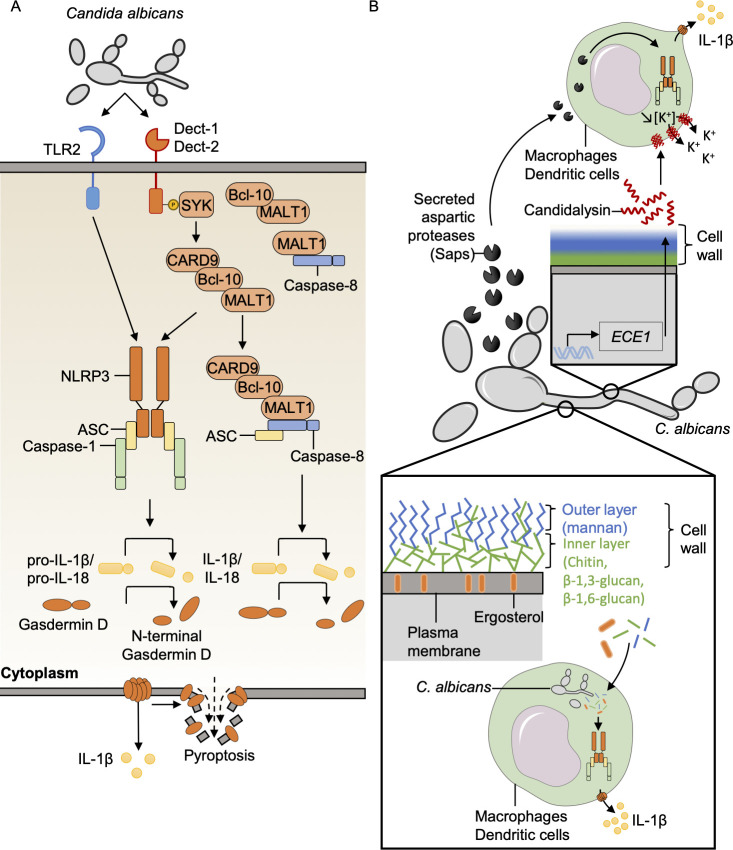
Fig 1. Mechanisms of C. albicans-induced inflammasome activation.
(A) C. albicans is recognized by TLRs and Dect receptors to mediate efficient priming and inflammasome activation. The CLR pathway is activated via the adaptor protein SYK, and the downstream supramolecular complex CARD9–Bcl-10–MALT1 drives the recruitment of caspase-8/ASC and/or NLRP3/ASC/caspase-1 to cleave gasdermin D and process and release IL-1β. (B) PAMPs and toxins from C. albicans that can activate the inflammasome have been identified. The C. albicans Saps mediate inflammasome activation. During germination of C. albicans, ECE1 regulates candidalysin toxin production and secretion; candidalysin forms pores in the host cell membrane and induces potassium efflux to cause canonical NLRP3 inflammasome activation. The cell wall, composed of an inner layer (Chitin/β-1,3-glucan/β-1,6-glucan) and an outer layer (mannan), participates in inflammasome activation. ASC, apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a caspase activation and recruitment domain; Bcl-10, B-cell lymphoma/leukemia 10; CARD9, caspase activation and recruitment domain-containing protein 9; CLR, C-type lectin receptor; Dect, Dectin; IL-1β, interleukin 1 beta; IL-18, interleukin 18; MALT1, mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma translocation protein 1; NLRP3, nucleotide-binding domain and leucine-rich repeat family pyrin domain-containing 3; PAMP, pathogen-associated molecular pattern; Saps, secreted aspartic proteases; SYK, spleen tyrosine kinase; TLR, Toll-like receptor.