Figure 2.
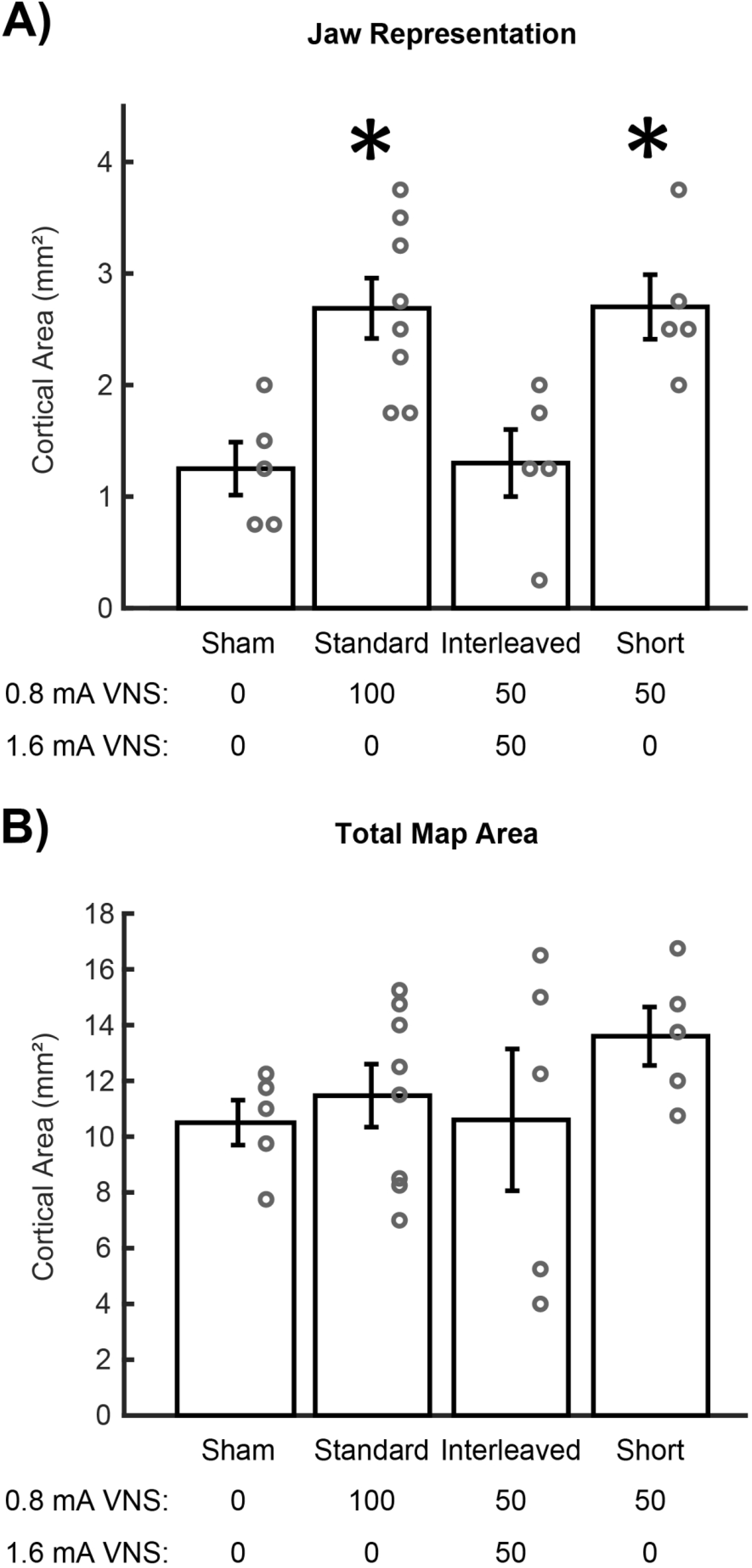
High intensity VNS disrupts cortical plasticity. (A) Standard VNS and Short VNS paired with chewing significantly increases jaw movement representation area in motor cortex compared to equivalent behavioral experience without VNS. Interleaved VNS fails to enhance plasticity. (B) No change in total motor cortex area was observed between groups. Bars represent mean ± SEM. “*” indicates p < 0.008.
