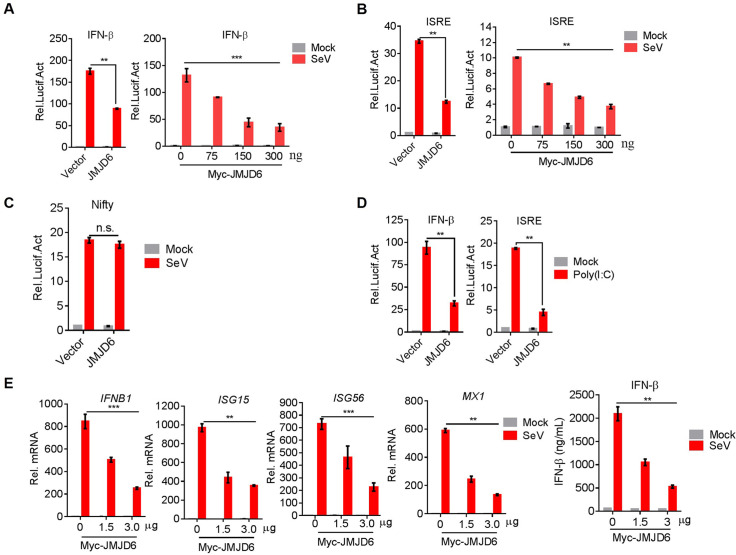
Fig 1. JMJD6 attenuates the type I interferon production.
(A) JMJD6 suppresses SeV-induced transcriptional activation of the IFN-β promoter in a dose-dependent manner. HEK293T cells were transfected with Myc-JMJD6 or empty vector together with the IFN-β luciferase reporters. At 24 h post-transfection (hpt), cells were mock-infected or infected with SeV for 12 h, and luciferase assays were performed 12 h later using a dual-specific luciferase assay kit. Statistical significance was determined with a two-tailed Student’s t-test (*** P<0.001, **P<0.01, and *P<0.05). (B) JMJD6 inhibits SeV-induced transcriptional activation of the ISRE promoter in a dose-dependent manner. HEK293T cells were transfected with the indicated plasmids and then mock-infected or infected with SeV for 12 h. Luciferase assays were performed using a dual-specific luciferase assay kit. (C) The effect of JMJD6 on SeV-induced transcriptional activation of the Nifty promoter. (D) JMJD6 suppresses poly(I:C)-induced transcriptional activation of IFN-β promoter and ISRE. HEK293T cells were transfected with Myc-JMJD6 or empty vector together with the IFN-β or ISRE luciferase reporters. At 24 hpt, cells were transfected by lipofectamine 2000 with or without poly(I:C) (50 ng/mL) for 12 h. Luciferase assays were performed with a dual-specific luciferase assay kit. (E) JMJD6 inhibits the transcription and secret of IFN-β and the transcription of its downstream ISGs in a dose-dependent manner. The mRNA levels of IFN-β, ISG15, ISG56, and MX1 were detected by qPCR. The IFN-β production was detected by ELISA.