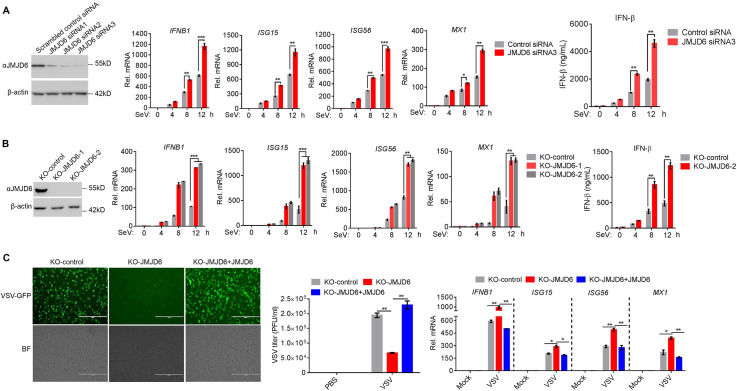
Fig 2. JMJD6 deficiency potentiates the type I interferon production.
(A) Evaluation of the knockdown efficiency of JMJD6-siRNA. HEK293T cells were transfected with 150 nM NC or si-JMJD6, and the expression of the JMJD6 protein was detected by immunoblotting using an anti-JMJD6 antibody (Left panel). Effects of si-JMJD6 on SeV-stimulated induction of the expression of IFN-β and its known downstream ISG genes. The mRNA levels of IFN-β, ISG15, ISG56, and MX1 were detected by qPCR. The IFN-β production was detected by ELISA (Right panel). (B) Immunoblotting analysis of JMJD6 protein levels in KO-JMJD6 HeLa cells (Left panel). Effects of KO-JMJD6 on SeV-stimulated induction of the expression of IFN-β and its known downstream ISG genes (Right panel). (C) Effects of JMJD6 on the replication of vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV). KO-control cells, KO-JMJD6 cells, or KO-JMJD6 cells reconstituted with JMJD6 were infected with VSV-GFP (MOI = 0.01) for 24 h, and viral infection and titers were detected using fluorescence microscopy and plaque assay, and the ISG56, MX1, ISG15, and IFN-β mRNAs was detected by qPCR.