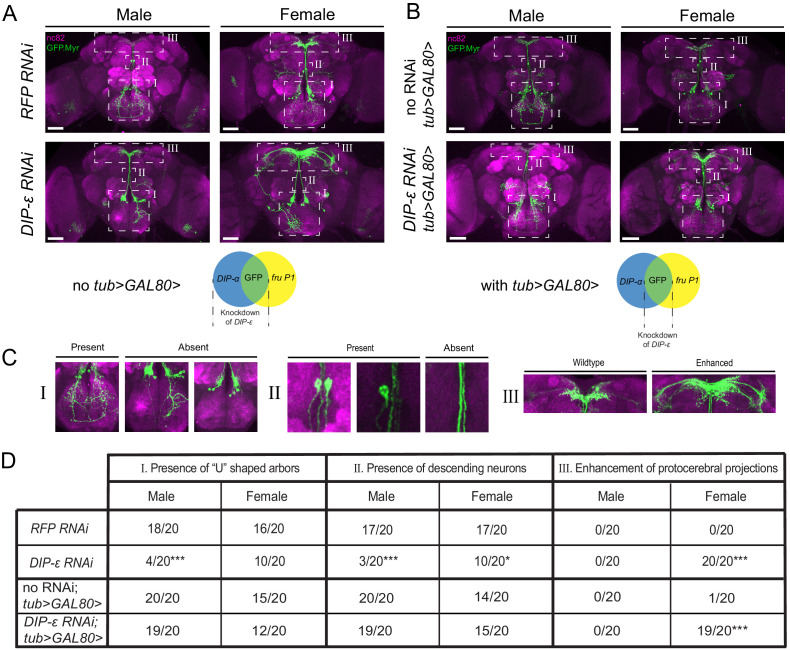
Figure 10. RNAi mediated knockdown of DIP-ε in fru P1 ∩ DIP-α neurons results in perturbations.
Maximum intensity projections of brains of 4–7 days old adult flies showing fru P1 ∩ DIP-α neurons stained with anti-GFP (green; rabbit α-GFP Alexa Flour 488) and the neuropil marker nc82 (magenta; mouse α-nc82, Alexa Flour 633). (A) fru P1 ∩ DIP-α neurons with DIP-ε or RFP (control) knockdown in all DIP-α expressing neurons. Genotypes are DIP-α Gal4; UAS > stop > GFP.Myr / RNAi; fruFLP / + with RNAi indicating either RFP or DIP-ε RNAi. (B) fru P1 ∩ DIP-α neurons with DIP-ε or no knockdown (control) restricted to only the visualized neurons (GFP+) through use of tub>GAL80>. Genotypes are DIP-α Gal4; UAS > stop > GFP.Myr / RNAi; fruFLP / tub>GAL80> with RNAi indicating either DIP-ε or no RNAi. The neuronal populations with RNAi expression are illustrated in the Venn diagrams. White dashed boxes indicate phenotypes of interest, which are located in (C) and include (subpanel I) presence of the U-shaped arbors, (subpanel II) presence of at least one descending neuron, and (subpanel III) enhancement of protocerebral projections. All phenotypes were scored blind and are quantified in (D). Statistical significance in between control flies and DIP-ε RNAi flies was evaluated by the Fisher’s exact test. In this figure, signicance is indicated as follows: *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. n = 20 brains for each category. Magnification is ×20 and scale bars represent 50 µM.