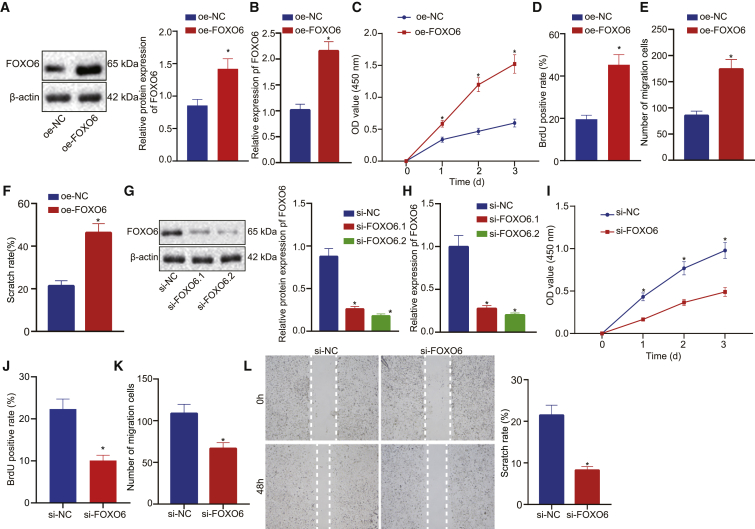
Figure 2.
FOXO6 enhanced cell proliferation and migration.
(A) FOXO6 protein expression normalized to β-actin detected by western blot analysis. oe-FOXO6 indicates FOXO6 overexpression; oe-NC indicates negative control. (B) FOXO6 mRNA expression detect by qRT-PCR. (C) CCK-8 assays detected the effect of overexpression FOXO6 on the growth of EC cells. (D) BrdU assays detected the effect of overexpression FOXO6 on the proliferation of EC cells. (E) Transwell assays detected the effect of overexpressed FOXO6 on the migration of EC cells. (F) Wound healing assays detected the effect of overexpressed FOXO6 on the migration of EC cells. (G) FOXO6 protein expression normalized to β-actin was examined by western blot analysis. (H) FOXO6 mRNA expression was detected by qRT-PCR. (I) CCK-8 assays detected the effect of FOXO6 knockdown on the growth of EC cells. (J) BrdU assays detected the effect of FOXO6 knockdown on the proliferation of EC cells. (K) Transwell assays detected the effect of FOXO6 knockdown on the migration of EC cells. (L) Wound healing assays detected the effect of FOXO6 knockdown on the migration of EC cells. Measurement data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation and compared by an independent sample t test between two groups and by a two-way ANOVA at different time points. The experiment was repeated three times independently. ∗p < 0.05 versus the oe-NC group or the si-NC group.