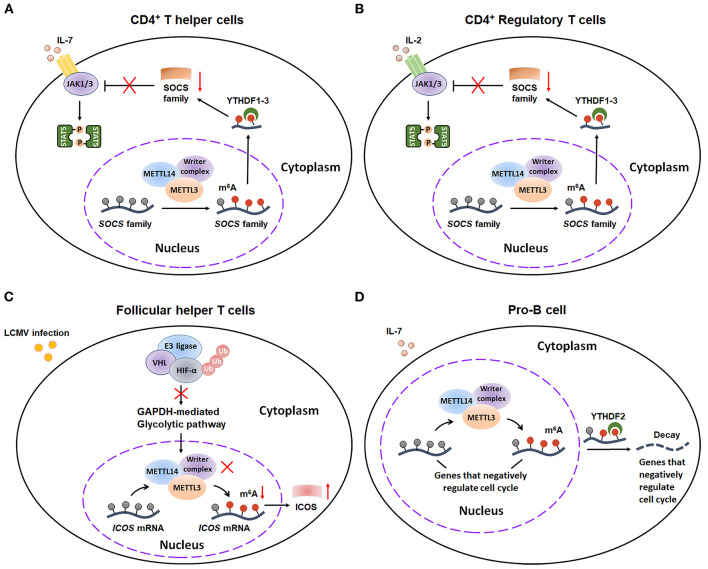
Figure 6.
m6A methylation plays a critical role in adaptive immunity. (A) m6A modification can promote the CD4+ T helper cells proliferation and differentiation by decaying SOCS mRNAs and consequently activating IL-7-STAT5 pathway. (B) m6A methylation plays an essential role in sustaining the suppressive functions of CD4+ T Regulator cells by decaying SOCS mRNAs and consequently activating IL-2-STAT5 pathway. (C) E3 ligase VHL promotes the early initiation of Tfh cells development via suppressing HIF-1α-GAPDH–mediated glycolysis, ultimately enhancing ICOS expression by reducing m6A-labed ICOS mRNA. (D) METTL14-mediated m6A modification facilitates IL-7-induced pro-B cell proliferation by decreasing a group of transcripts that negatively regulate cell cycle. SOCS, suppressor of cytokine signaling; JAK, Janus Kinase; STAT5, Signal transducer and activator of transcription 5; VHL, Von Hippel–Lindau; HIF-1α, hypoxia-inducible factor 1α; ICOS, inducible T cell costimulatory; Ub, Ubiquitination.