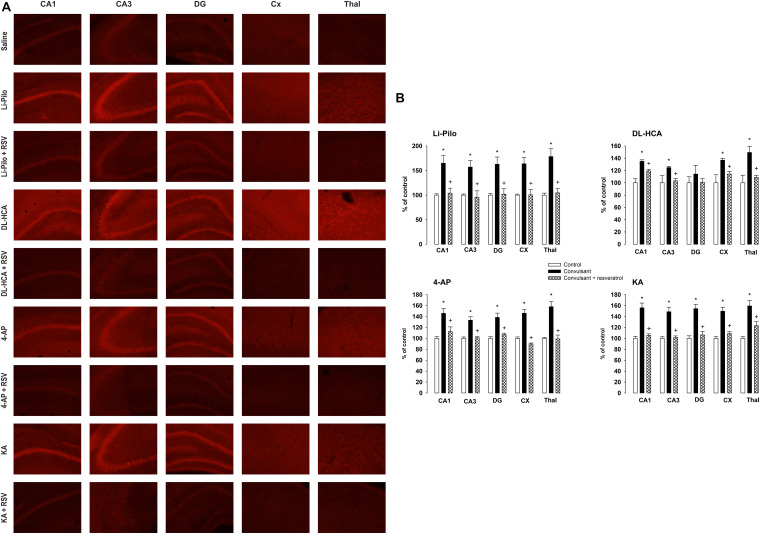
FIGURE 3.
(A) Fluorescence of the oxidized products of hydroethidium (reflecting superoxide anion production), assessed microscopically by fluorescence (>600 nm), in various brain structures following 60 min lasting SE induced by Li-Pilocarpine (Li-Pilo), homocysteic acid (DL-HCA), 4-aminopyridine (4-AP) or kainic acid (KA). Upper image for each model, convulsant agent alone; lower image for each model, convulsant agent plus resveratrol. (B) Effect of resveratrol on superoxide anion formation at 60 min following the onset of SE, induced in immature rats by Li-Pilo, DL-HCA, 4-AP, or KA. White columns, saline-treated controls; black columns, convulsant agent alone; cross-hatched columns, convulsant agent plus resveratrol. Results are expressed in percent, compared to 100% in the control animals. Mean values for 5–6 animals ± SEM. *P < 0.05 as compared with saline; †P < 0.05 as compared with convulsant agent alone. CA1 and CA3, hippocampal fields; DG, dentate gyrus; CX, cerebral cortex; Thal, dorsal thalamus.