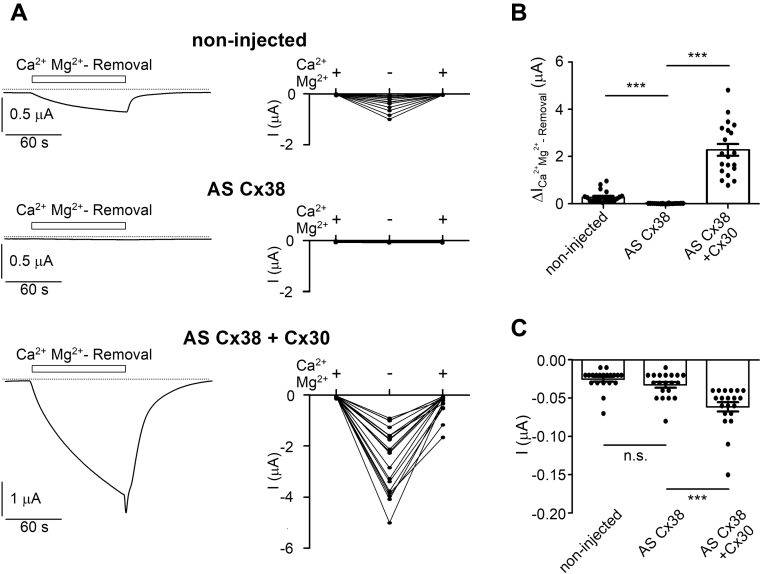
Figure 1.
Inhibition of endogenous Cx38 and functional expression of human Cx30 in Xenopus laevis oocytes. A, Left panels, representative traces demonstrating the effect of divalent cation removal on whole-cell currents recorded at a holding potential of −60 mV in noninjected oocytes, oocytes injected with antisense oligoDNA against endogenous Cx38 (AS Cx38) or coinjected with AS Cx38 and human Cx30 cRNA (AS Cx38 + Cx30). Bath solution contained 1.8 mM Ca2+ and 1 mM Mg2+ or was nominally free of Ca2+ and Mg2+ and contained 2 mM EDTA for the time intervals (100 s) indicated by open bars (Ca2+Mg2+- Removal). Dashed lines indicate zero current level. Right panels, baseline inward currents in standard Ca2+and Mg2+-containing bath solution (left +), maximum inward currents in the absence of divalent cations (−), and minimum inward currents reached after reapplication of Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions (right +) from similar experiments as shown in left panels (n = 20; N = 2). Lines connect data points from individual oocytes. B, data from the experiments shown in (A) are summarized by subtracting the baseline current values in the presence of divalent cations from the corresponding maximal current value reached after Ca2+ and Mg2+-removal (ΔICa2+Mg2+-Removal). C, summary of baseline current values recorded at the beginning of each experiment in the presence of Ca2+ and Mg2+ in the bath solution. Mean ± SEM and data points for individual oocytes are shown; ∗∗∗p < 0.001; n.s., not significant; Kruskall–Wallis with Dunn’s post hoc test.