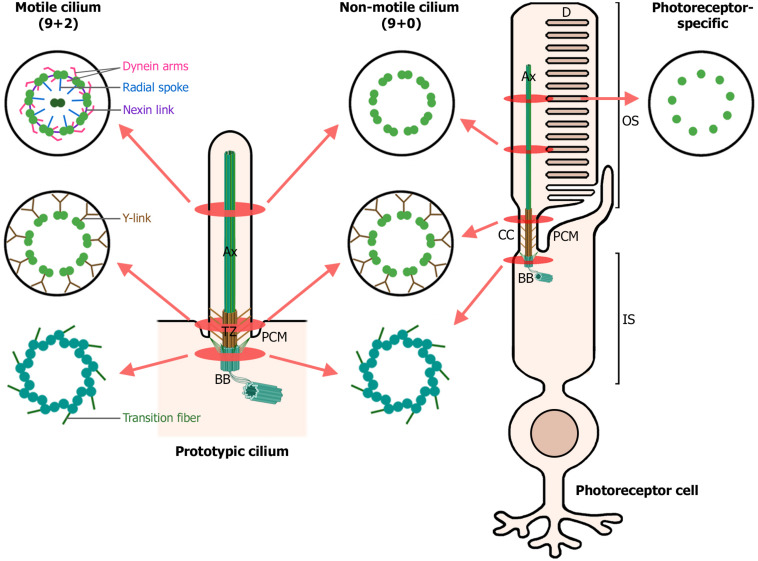
FIGURE 1.
Structure of motile, non-motile, and photoreceptor cilia. The left diagram depicts a prototypic cilium with its main compartments: the axoneme (Ax), transition zone (TZ) with its Y-links, periciliary membrane (PCM) and the basal body (BB). The right diagram depicts a rod photoreceptor, which in addition, displays photoreceptor-specific cellular structures: the outer segment (OS), comprising the membranous disks (D) and the axoneme; the connecting cilium (CC), analogous to the transition zone in primary cilia; and the inner segment (IS), which contains the basal body and most cellular organelles. Cross-sections through the ciliary compartments of both motile and non-motile cilia are shown: the basal body triplet microtubules with their transition fibers, shared by motile cilia, non-motile cilia and photoreceptor primary cilia; the transition zone of motile and non-motile cilia and the analogous connecting cilium in photoreceptors; the axonemal microtubule doublets, decorated with dynein arms, radial spokes and nexin links in motile cilia; and finally, the axonemal microtubule singlets characteristic of photoreceptor primary cilia. (Figure created with BioRender.com).