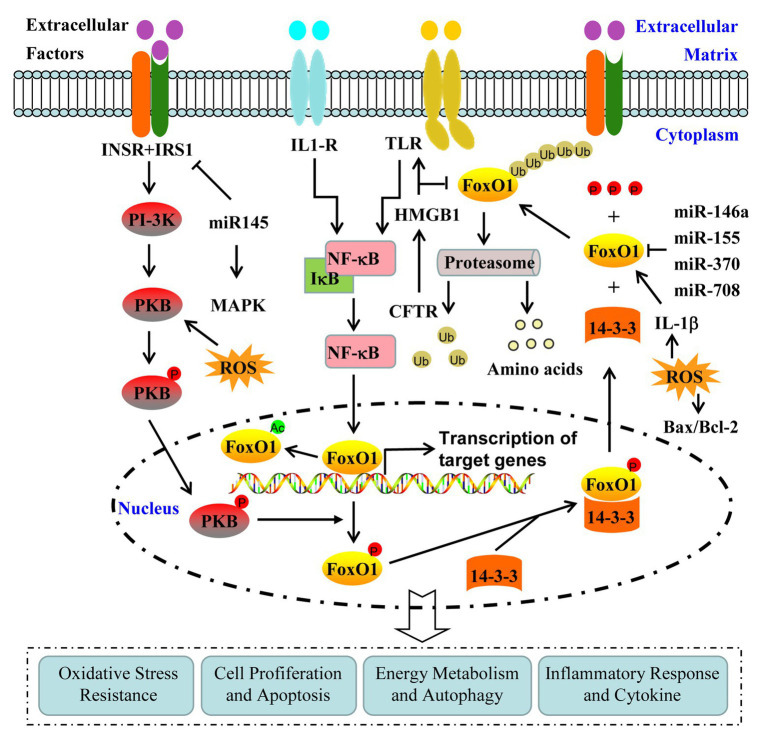
Figure 1.
Regulation and contribution of FoxO1 activity in the pathogenesis of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). FoxO1 activity is mainly regulated by the post-translational modifications, including phosphorylation, acetylation, and ubiquitination. FoxO1 is involved in the pathogenesis of PCOS through various signaling pathways, including phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI-3K)/protein kinase B (PKB), mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), high-mobility group box 1(HMGB1)/Toll-like receptor 4(TLR4)/nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB), and Interleukin-1β (IL-1β).