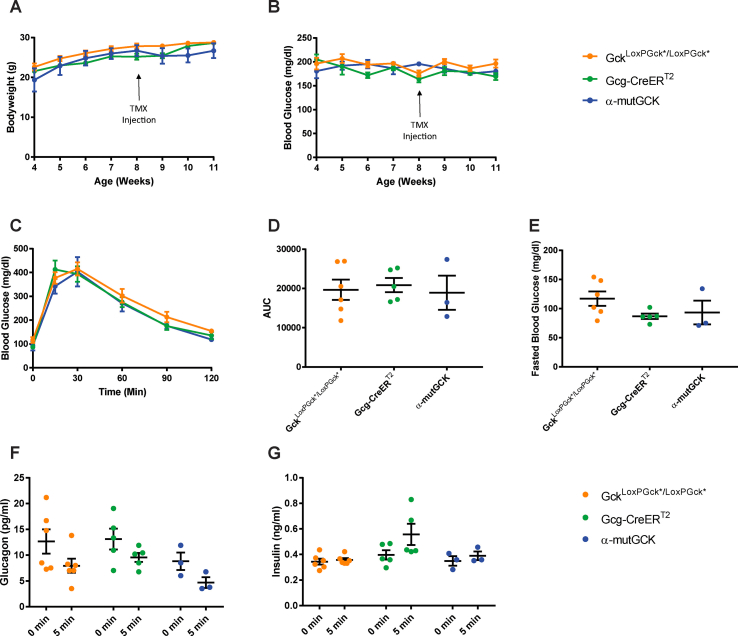
Figure S5.
Determination of the effects of α-cell GCK activation on glucose homeostasis in adult male mice (separated control groups from Figure 1). (A) Body weights of α-cell GCK mutant and control mice (n = 4 for α-mutGCK, n = 6 for GckLoxPGck∗/LoxPGck∗, and n = 5 for Gcg-CreERT2). (B)Ad libitum blood glucose for α-cell GCK mutant and control mice (n = 4 for α-mutGCK, n = 6 for GckLoxPGck∗/LoxPGck∗, and n = 5 for Gcg-CreERT2). (C) Intraperitoneal glucose tolerance test (1 g/kg body weight) (n = 3 for α-mutGCK, n = 6 for GckLoxPGck∗/LoxPGck∗, and n = 5 for Gcg-CreERT2). (D) Area under the curve (AUC) and (E) fasted blood glucose measurements from intraperitoneal glucose tolerance test in (C). (F) Plasma glucagon and (G) plasma insulin in mice fasted or 5 min after glucose injection in (C).