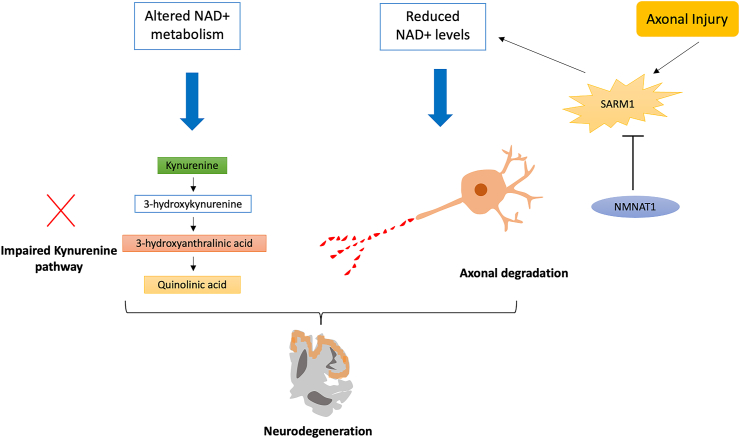
Figure 4.
Altered NAD metabolism is associated with neurodegeneration. Axonal injury leads to the activation of SARM1, which reduces NAD + levels and leads to axonal degeneration. The overexpression of NMNAT1 inhibits SARM1 and protects injured axons. NAD levels are associated with axonal degradation, and impairment in the KYN pathway causes fluctuations in KYN pathway metabolite levels, which impairs the neurotransmission process and leads to neurodegeneration and the development of neurological disorders [201].