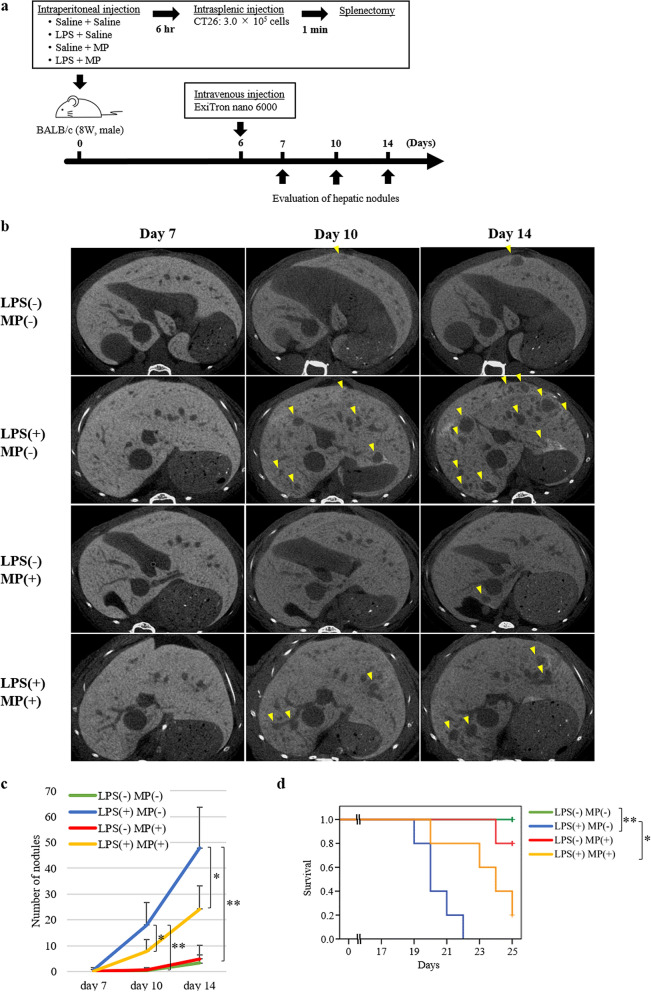
Figure 3.
Suppressive effects of MP in LPS-induced murine models of hepatic metastasis. (a) Mouse colon cancer cell line (CT26) hepatic metastasis model; male BALB/c mice (8 weeks old) were treated with saline/saline (control), LPS/saline, saline/MP, or LPS/MP. Six hours later, 3.0 × 105 CT26 cells were injected into the inferior pole of the spleen, followed by splenectomy 1 min later. The number of hepatic nodules was evaluated using enhanced micro-CT imaging on days 7, 10, and 14. (b) Representative CT images of the liver. Almost the same liver slice from the same individual in each group was photographed axially on days 7, 10, and 14. Yellow arrowheads indicate nodules with a diameter of more than 50 µm. (c) Metastatic nodules in the liver were quantified on days 7, 10, and 14. Data are means ± standard error (n = 5, each group); *P < 0.05, **P < 0.001. (d) Kaplan–Meier survival curves of each group of hepatic metastasis model mice. The horizontal axis represents the days from inoculation of tumour cells and the vertical axis represents the survival rate. Tick marks represent censored subjects. *Log-rank P < 0.05, **log-rank P < 0.01.