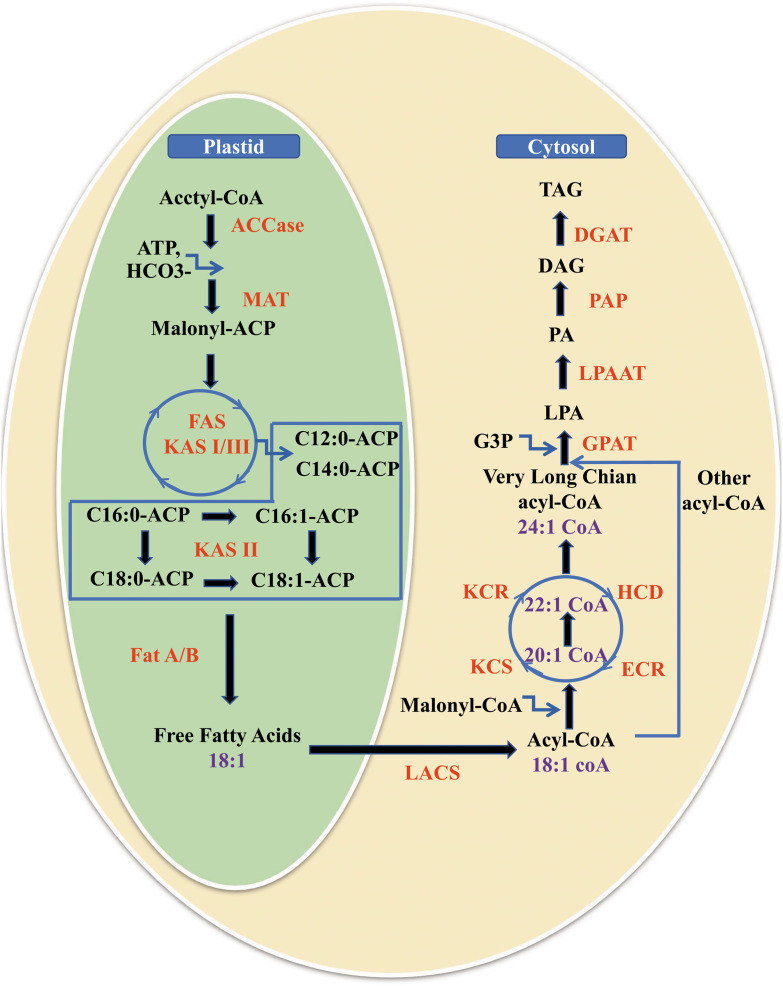
FIGURE 2.
Biosynthesis and accumulation of nervonic acid in plants. It includes the de novo fatty acid synthesis in plant plastids, fatty acid elongation from oleic acid (18:1 ω-9) to nervonic acid (24:1 ω-9) for 3 cycles with each cycle adding two carbon units using four core enzymes located at the endoplasmic reticulum membrane in the cytoplasm, and fatty acids storage as triacylglycerols by three key acyltransferases. MAT, malonyl-CoA/ACP transacylase; FAS, fatty acid synthase; KAS, ketoacyl-ACP synthase; Fat A/B, fatty acid thioesterases A/B; LACS, long chain acyl CoA synthetase; FAE, fatty acid elongase; KCS, 3-ketoacyl-CoA synthase; KCR, 3-ketoacyl-CoA reductase; HCD, 3-hydroxacyl-CoA dehydratase; ECR, trans-2,3-enoyl-CoA reductase; GPAT, glycerol-phosphate acyltransferase; G3P, glycerol-3-phosphate; LPA, lysophosphatidic acid; LPAAT, lysophosphatidic acid acyltransferase; PA, phosphatidic acid; PAP, phosphatidic acid phosphatase; DAG, diacylglycerol; DGAT, diacylglycerol acyltransferase; TAG, triacylglycerol.