Figure 1.
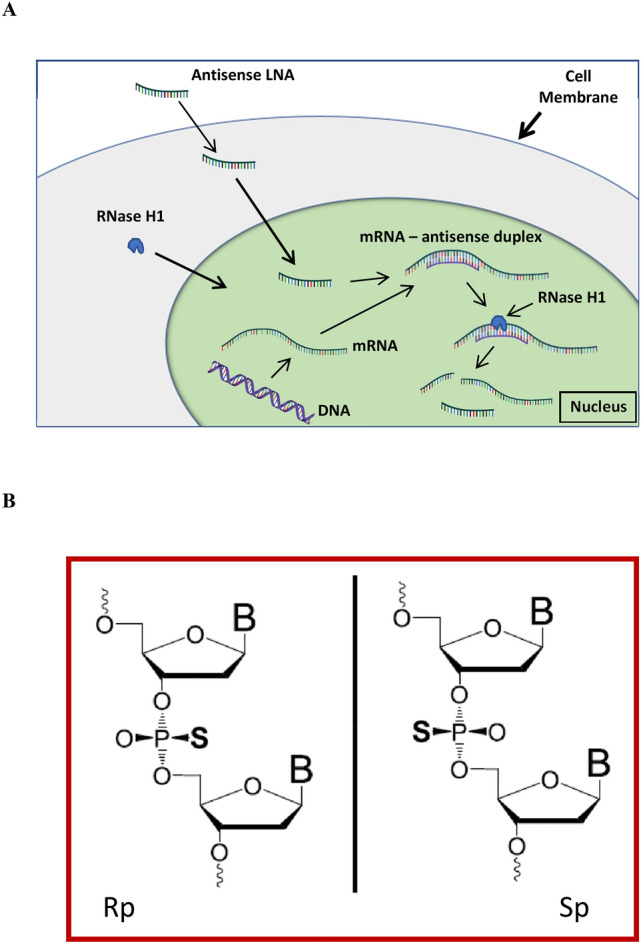
Antisense mechanism (A) and phosphorothioate (B). (A) The use of LNA oligonucleotides as inhibitors of disease—forming proteins, or reduction of harmful RNA, is based on specific hybridization to target mRNA. This duplex recruits the cellular enzyme RNase H1 that degrade the hybridized mRNA. The LNA oligonucleotide remains intact under this process and will repeatedly trigger degradation of further target mRNA; (B) the two steric configurations Rp and Sp of the phosphorothioate linkages between the nucleobases of phosphorothioate oligonucleotides.
