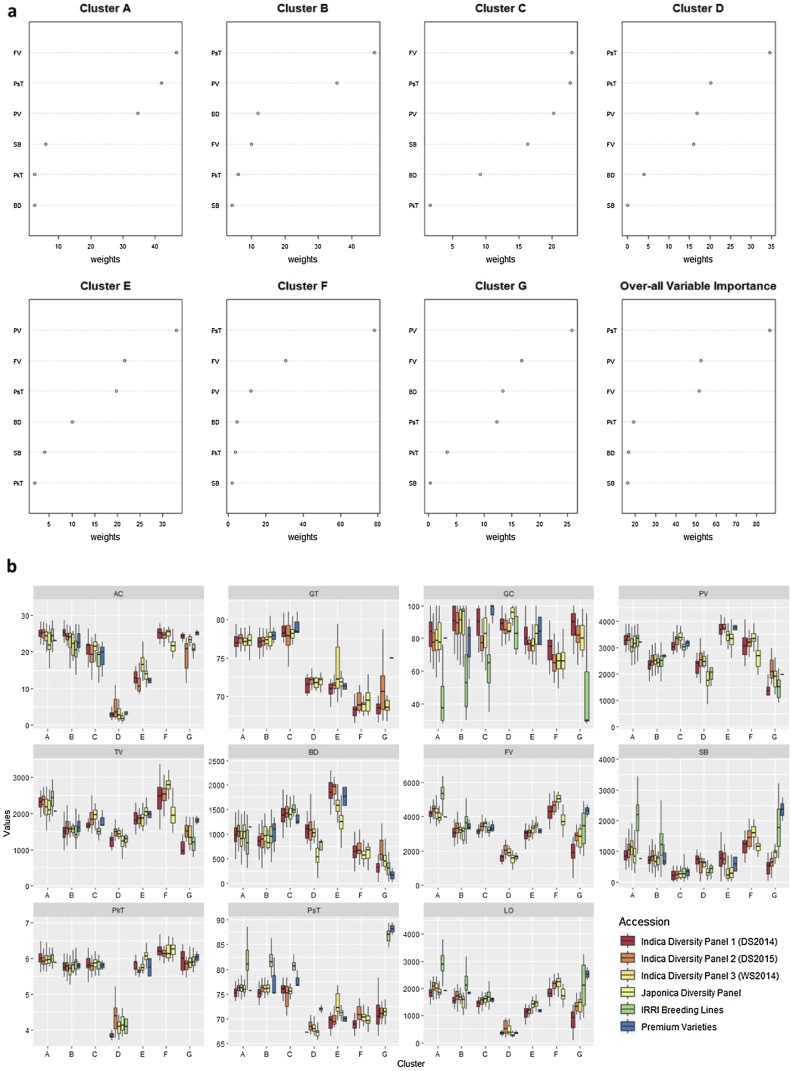
Fig. 1.
Classification modeling based on the RVA properties using Random Forest. (a) Important variables resulted from modeling based on mean decrease in accuracy and individual decrease in accuracy of each cluster. (b) Phenotypic distribution of selected lines from dry season of 2014 (Indica Diversity Panel 1, n = 301), 2015 (Indica Diversity Panel 2, n = 316), wet season of 2014 (Indica Diversity Panel 3, n = 318), japonica variety (Japonica Diversity Panel, n = 293) planted during the dry season of 2015, IRRI Breeding Lines (n = 106), and Premium Varieties (n = 11) presented as boxplots comparing the seven cluster created based on selected RVA parameters. Cluster labels are as follows: A, B, C, D, E, F, and G; Variable names are follows: amylose content (AC), gelatinization temperature (GT), gel consistency (GC), peak viscosity (PV), trough viscosity (TV), breakdown viscosity (BD), final viscosity (FV), setback viscosity (SB), peak time (PkT), pasting temperature (PsT) and lift-off viscosity (LO), AM1 (Amylose 1), AM2 (Long-chain Amylopectin), MCAP (Medium-chain Amylopectin), SCAP (Short-chain amylopectin).