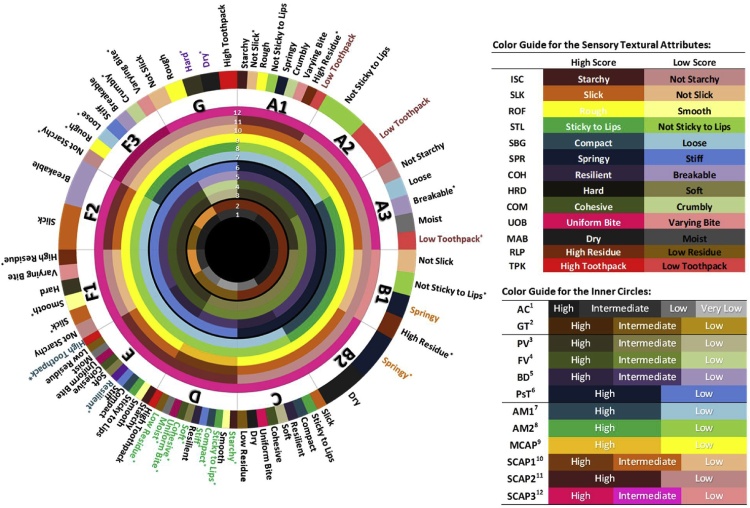
Fig. 4.
Rice texture wheel chart for each clusters with their corresponding sensory descriptions. The description in the outer circle highlighted in colors is the sensory description for each ideotype and the wheel chart also features some of the routine quality, RVA, and starch structure parameters that are deemed important both in modeling and classification. The sensory characteristics in the wheel chart marked with an asterisk (*) was the ideotype which received either the minimum or the maximum score in that particular attribute. For example A1 has the lowest score for slickness, while F1 got the highest score for the same attribute. Variable names are follows: amylose content (AC), gelatinization temperature (GT), gel consistency (GC), peak viscosity (PV), trough viscosity (TV), breakdown viscosity (BD), final viscosity (FV), setback viscosity (SB), peak time (PkT), pasting temperature (PsT) and lift-off viscosity (LO), AM1 (Amylose 1), AM2 (Long-chain Amylopectin), MCAP (Medium-chain Amylopectin), SCAP1(Short-chain amylopectin, 36 > DP > 21), SCAP2(Short-chain amylopectin, 20 > DP > 13), SCAP3(Short-chain amylopectin, 12 > DP > 6), initial starchy coating (ISC), slickness (SLK), roughness (ROF), stickiness to lips (STL), stickiness between grains (SBG), springiness (SPR), cohesiveness (COH), hardness (HRD), cohesiveness of mass (COM), uniformity of bite (UOB), moisture absorption (MAB), residual loose particles (RLP), and toothpack (TPK) were generated.