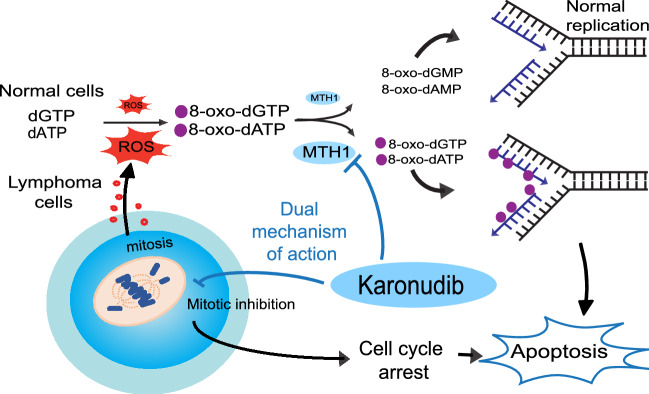
Figure 7.
Dual mechanism of karonudib leads to apoptosis in lymphoma cells. Karonudib was developed to target the nucleotide metabolism by inhibiting the nucleotide pool sanitizing enzyme, MTH1. MTH1 converts oxidized nucleotide triphosphates created by reactive oxygen species (ROS) to the corresponding monophosphate forms, preventing incorporation of oxidized nucleotides into DNA. High ROS levels in lymphoma corresponds to high MTH1 levels. Karonudib inhibits the function of MTH1 and results in increased oxidized nucleotides in the DNA, and the drug also perturbs microtubule polymerization and leads to cell cycle arrest and apoptosis.