fig 1.
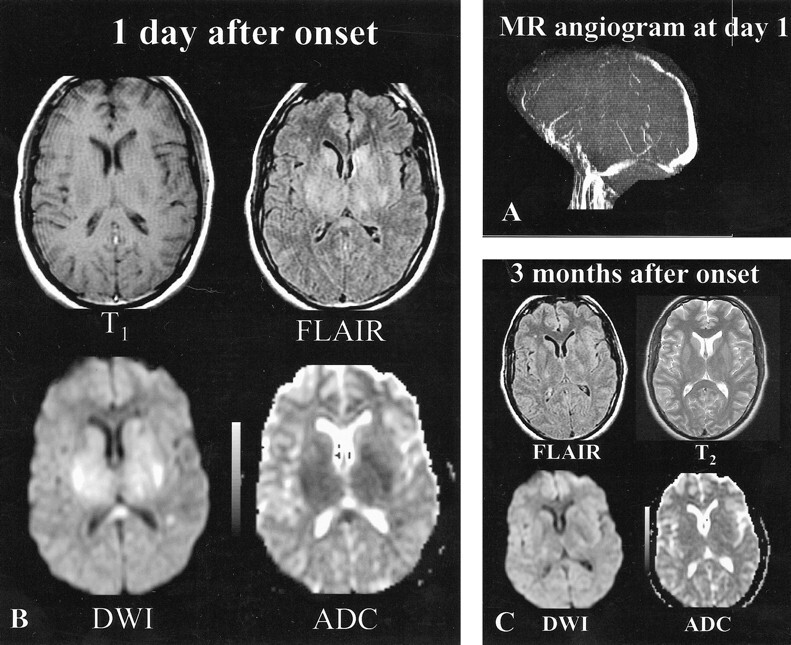
Patient 9, a 34-year-old woman with headaches, cognitive function loss, and sudden-onset right hemiparesis.
A, MR angiogram (axial 2D time-of-flight method, maximum intensity pixel reconstruction, lateral view), obtained 1 day after the onset of neurologic symptoms, shows an occlusion of the deep and superficial venous systems (vein of Galen, straight sinus, internal cerebral veins, anterior part of the superior sagittal sinus).
B, Initial MR image obtained 1 day after the onset of neurologic symptoms. Axial spin-echo T1-weighted image shows bilateral areas of hypointensity at the level of the capsulae. Initial fast-FLAIR (10002/148/2200 [TR/TE/TI]) and diffusion-weighted (4000/120 [TR/TE], b = 1000 s/mm2) images show widespread bilateral areas of hyperintensity in putamen, caudate nuclei, and the capsulae. ADC maps show markedly decreased ADC values (0.33–0.42 10−3 mm2/s) (ie, z scores <−3 when compared with normal-appearing brain).
C, Follow-up MR image obtained 3 months after onset shows normal-appearing brain at the level of the gray nuclei, indicating that most lesions with initially decreased ADC values were reversible. Only focal slight areas of hyperintensity were visible in the centrum semiovale (not shown). Symptoms regressed completely within a few weeks.
