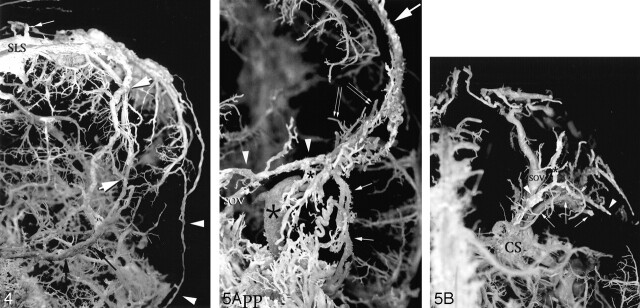
Fig 4.
Anterior and lateral view of the left convexity of a corrosion cast showing the parietal portion of the anterior branch of the middle meningeal veins. The dual meningeal and diploic nature of the parietal portion of the anterior branch of the middle meningeal veins is demonstrated. The anterior parietal diploic vein (black arrows) and the parietal portion of the anterior branch of the middle meningeal veins may be individualized wherever their course does not overlap. Note how diploic veins enter the venous lacunae of the superior longitudinal sinus at a right angle (white arrow). A parietotemporal diploic vein is demonstrated (white arrowheads); it drained into the middle third of the left transverse sinus.
Fig 5. Corrosion cast specimens illustrating the venous structures in the region of the lesser sphenoid wing.
A, Anteroposterior view of left side of a corrosion cast showing the sinus of the lesser sphenoid wing (arrowheads), the parietal portion of the anterior branch of the middle meningeal veins (large arrow), and the sphenoid portion of the anterior branch of the middle meningeal veins (small arrows). Different branches of the superficial middle cerebral vein (double arrows) are seen behind the sinus of the lesser sphenoid wing. The superficial middle cerebral vein drains into a paracavernous sinus (large asterisk). The sinus of the lesser sphenoid wing is seen to cross over the superior ophthalmic vein (SOV). Only the dorsal aspect of the superior ophthalmic vein was filled in this side. Note the different aspects of the sphenoid and parietal portions of the anterior branch of the middle meningeal veins, in which the former offers a typical aspect of parallel meningeal channels, whereas the latter resembles a diploic vein. A diploic vein of the greater sphenoid wing (small asterisks) is seen to drain into the pterygoid plexus.
B, Superior view of the right side of a corrosion cast in the region of the right lesser sphenoid wing, demonstrating the sinus of the lesser sphenoid wing (white arrowheads), the diploic vein of the orbital roof (asterisk; the anterior portion of this vein is not filled), and the superficial middle cerebral vein (arrows) draining into a lateral wall of a cavernous sinus (not seen). Note how the superficial middle cerebral vein and the sinus of the lesser sphenoid wing are not connected and course on different anatomic planes. The sinus of the lesser sphenoid wing typically crosses over the dorsal portion of the superior ophthalmic vein. The anterior branch of the middle meningeal veins was not filled in this side. SOV signifies superior ophthalmic vein; CS, cavernous sinus; SLS, superior longitudinal sinus.