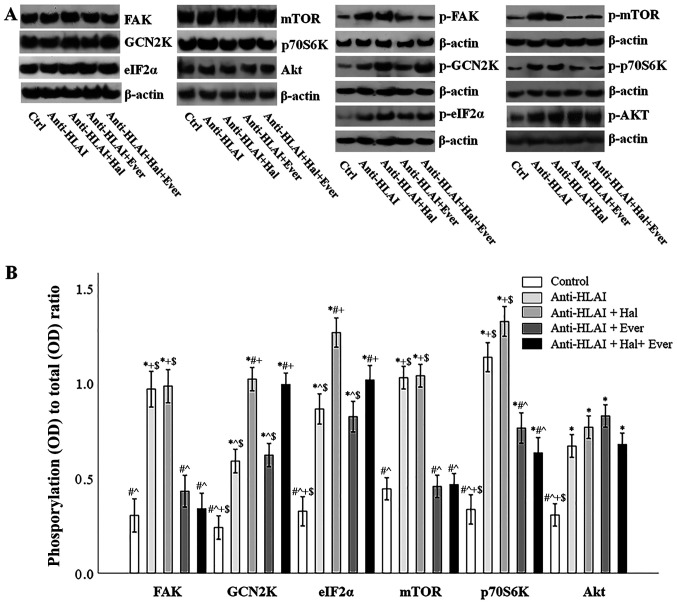
Figure 3.
Effect of anti-HLAI on integrins, mTOR and GCN2K signal transduction and the impact of halofuginone or everolimus. (A) Representative experiment for the expression of total and phosphorylated FAK, GCN2K, eIF2α, mTOR, p70S6K and AKT. (B) Cumulative results depict the phosphorylated to total protein ratio and revealed that anti-HLAI antibodies increased p-FAK, p-GCN2K, p-eIF2α, p-mTOR, p-p70S6K and p-AKT levels. Halofuginone increased p-GCN2K and p-eIF2α. Everolimus treatment decreased the anti-HLAI antibody-induced upregulation of p-FAK, p-mTOR and p-p70S6K. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM. *P<0.05 vs. control cells, #P<0.05 vs. anti-HLAI-treated cells, ^P<0.05 vs. anti-HLAI-treated cells administered halofuginone, +P<0.05 vs. anti-HLAI-treated cells administered everolimus and $P<0.05 vs. anti-HLAI-treated cells with halofuginone and everolimus. HLAI, human leukocyte antigen class I; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; GCN2K, general control nonderepressible 2 kinase; FAK, focal adhesion kinase; eIF2α, eukaryotic initiator factor 2α; p, phosphorylated; Hal, halofuginone; Ever, everolimus; Ctrl, control; OD, optical density.