fig 2.
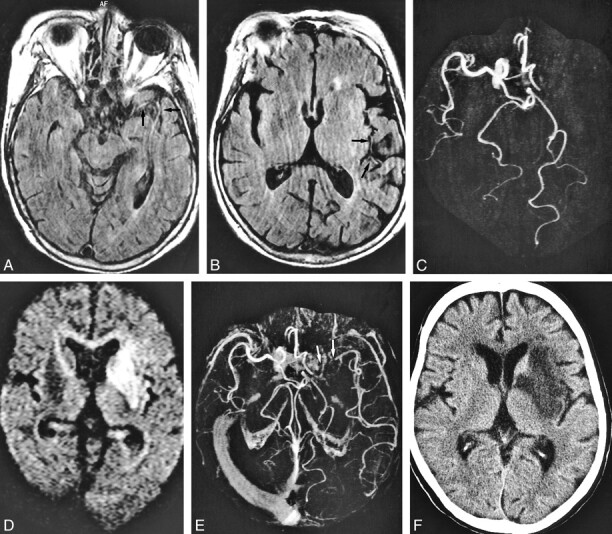
A 71-year-old woman who underwent imaging 7 hours after onset of right hemiparesis and aphasia.
A and B, FLAIR images (8000/10/1, TI = 2000) show intraarterial signal in M1, M2, and M3 segments of the left middle cerebral artery (arrows).
C, MR angiogram (32/6.8, flip angle = 15 degree) demonstrates lack of TOF in the left internal carotid and middle cerebral arteries.
Perfusion imaging (not shown) showed a hypoperfused area with increased time-to-peak and mean transit time values in the left middle cerebral artery territory as large as the area of intraarterial signal distribution and lack of TOF.
D, Diffusion-weighted image (500/123/1, b = 1200) shows hyperintense lesion in the left basal ganglia and insular cortex.
E, Postcontrast MR angiogram (32/6.8, flip angle = 15 degrees) shows intraluminal enhancement in the left middle cerebral artery except for in the M1 segment. Arrow indicates complete obstruction in the left M1 segment.
F, Final infarction is confirmed in the basal ganglia and insular cortex by CT performed 9 days after stroke symptom onset, corresponding to the initial lesion seen on diffusion-weighted images.
Note lesion in D is smaller than the area of intraarterial signal distribution. Intraarterial signal consists of not only complete obstruction but also slow collateral circulation. The area of final infarct is smaller than that of intraarterial signal distribution. Ischemic penumbra may be present in the mismatch between the intraarterial signal distribution and the diffusion-weighted lesion.
