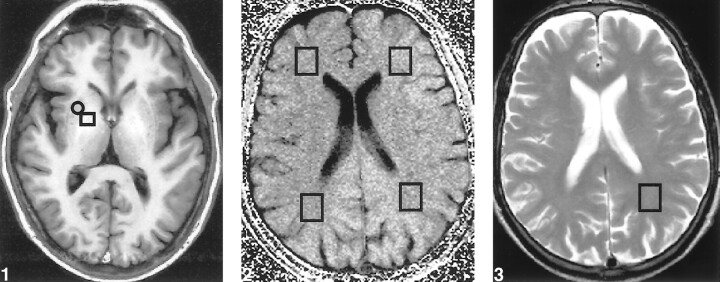
fig 1.
Transverse T1-weighted image (inversion recovery spin-echo; 1500/20; inversion time, 650 ms; number of acquisitions, one), obtained at the level of the basal ganglia in a patient with liver cirrhosis, shows bilateral increased signal in the globus pallidus. For calculating the globus pallidus index, mean signal intensity was calculated from a region of interest localized in both the putamen (□) and globus pallidus (○).fig 2. Transverse MTR map of a supraventricular level, obtained from two proton density gradient-echo sequences (714/12; flip angle, 20 degrees; number of acquisitions, one), the first with and the second without an off-resonance preparation pulse. MTR values were obtained from four different voxels (□) located in otherwise normal-appearing white matter, as defined on the T2-weighted sequence, within both parietal and frontal lobes.fig 3. Axial T2-weighted image (fast spin-echo; 3550/90; number of acquisitions, two), obtained at a supraventricular level, shows the voxel from which the 1H-MRS image was obtained in the normal appearing white matter in the parietal lobe