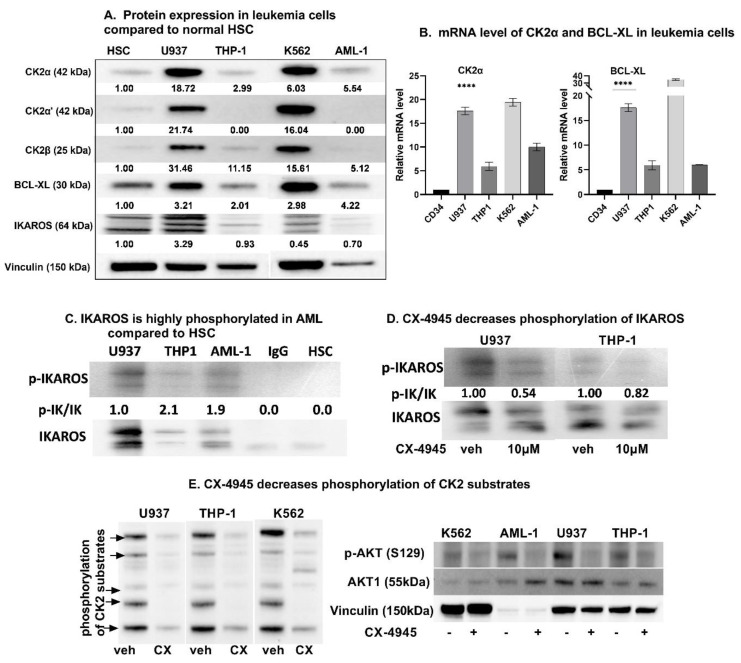
Figure 1.
CK2 overexpression in AML cells causes IKAROS phosphorylation which is reversed by CK2 inhibitor, CX-4945. (A) Baseline protein levels of CK2α, CK2α’, CK2β, IKAROS and BCL-XL in the myeloid leukemia cell panel [U937, THP-1, K562, and primary AML cells (labelled AML-1) were measured by western blot and compared to CD34+ Hematopoietic Stem Cells (HSC). Multiple IKAROS bands represent Ikaros isoforms 1 and 2. (B) qRT-PCR showing mRNA level of CK2α and BCL-XL in various AML cells compared to CD34+ HSC. **** (p < 0.0001). (C) Radio-blot showing increased Phosphorylated IKAROS (p-IKAROS) in AML cells compared to HSC. (D) Radio-immunoblot showing dose-dependent decrease in Phospho-IKAROS level following CX-4945 treatment. U937 and THP-1 were treated with 10 µM and AML-1 was treated with 5μM (IC50–3.791 μM) CX-4945 for 48 h. IC50 values of CX-4945 treated cells are shown in Figure S2. (E) Western blot showing decrease in amount of phosphorylated CK2 substrates with molecular masses of approximately 175, 120, 80, 70 and 56 kDa as indicated by arrows (left panel) and western blot showing phosphorylation extent of specific CK2 substrate, AKT1 at Ser129 (right panel).