FIG 1.
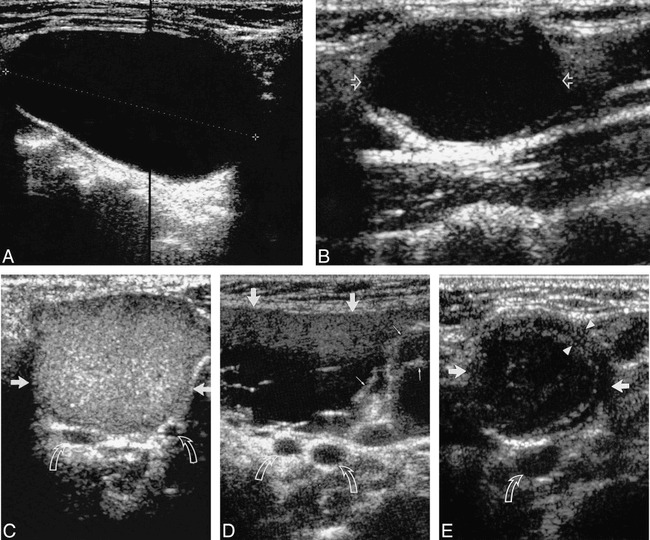
A, Longitudinal sonogram of an anechoic second BCC (calipers) with posterior enhancement.
B, Longitudinal sonogram of a second BCC (open arrows), predominantly hypoechoic with faint internal debris. Note the presence of posterior enhancement.
C, Transverse sonogram of a second BCC (straight arrows) with homogeneous, hyperechoic, internal echoes (pseudosolid). Note the lack of posterior enhancement. Curved arrows identify the bifurcation of the carotid artery. Note that no portion of the cyst extends into carotid bifurcation.
D, Transverse sonogram of a second BCC (large arrows) with heterogeneous internal echoes, debris, and septa (small arrows). Note the lack of posterior enhancement. Curved arrows identify the bifurcation of the carotid artery. Note that no portion of the cyst extends into carotid bifurcation.
E, Transverse sonogram of a second BCC (straight arrows) with thick walls (arrowheads) and internal echoes. Note the lack of posterior enhancement. Curved arrow identifies the common carotid artery.
