Fig 1.
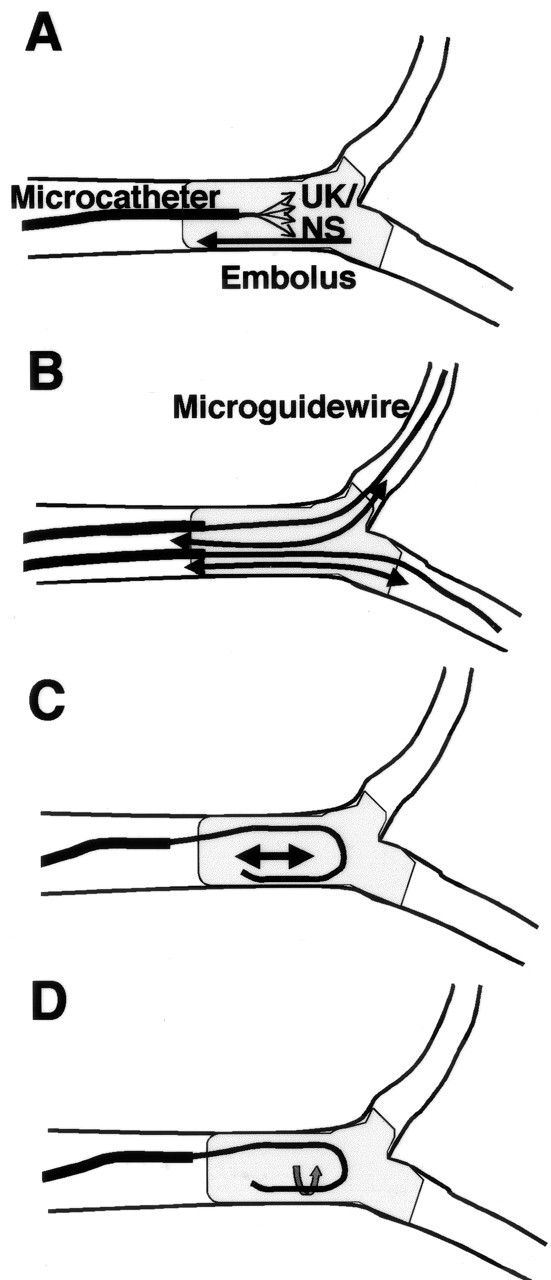
Techniques of mechanical disruption. A, Microcatheter tip is advanced to the distal end of the embolus. Urokinase in 10 mL of normal or heparinized normal sodium chloride solution is manually injected into the embolus as forcefully as possible while the tip is slowly withdrawn into the proximal end of the embolus. B, Microcatheter tip is passed back and forth through the clot over a microguidewire several times. For an embolus at a bifurcation, the microcatheter is introduced into both distal arteries to disrupt clot entering them. C, Tip of a double-angled microguidewire is flexed into a J shape in the arterial lumen near the embolus and moved gently in the embolus along the vasculature several times. D, Rotation of a J-shaped guidewire tip in the embolus several times.
