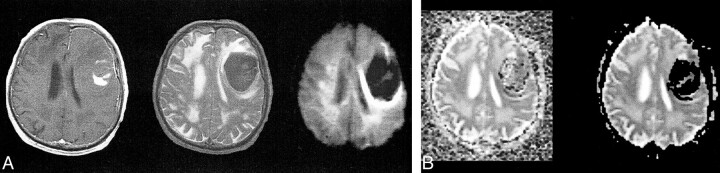
fig 2.
T2-dark left frontal acute hematoma (intracellular deoxyhemoglobin with some intracellular methemoglobin).
A, T1-weighted image (600/20/1) (left) shows predominantly isointense blood products (deoxyhemoglobin) with some areas of hyperintensity centrally (intracellular methemoglobin). Fast spin-echo T2-weighted image (4000/85/1) (middle) shows predominantly low signal intensity corresponding to intracellular blood products. Diffusion-weighted isotropic image (10000/125/1) (right) shows marked hypointensity relative to the brain. This would intuitively be expected to correspond to fast diffusion (compare with CSF in ventricles).
B, Trace ADC map displayed without background masking (left) shows hematoma to have diffusion rates comparable with the brain, with some dropped points at the periphery. The dropped points are caused by background noise variation resulting in negative ADC values. Note that the diffusion within the hematoma is neither restricted nor fast relative to the brain. Trace ADC map displayed with 2% background masking (right) shows dramatic loss of pixels within hematoma.