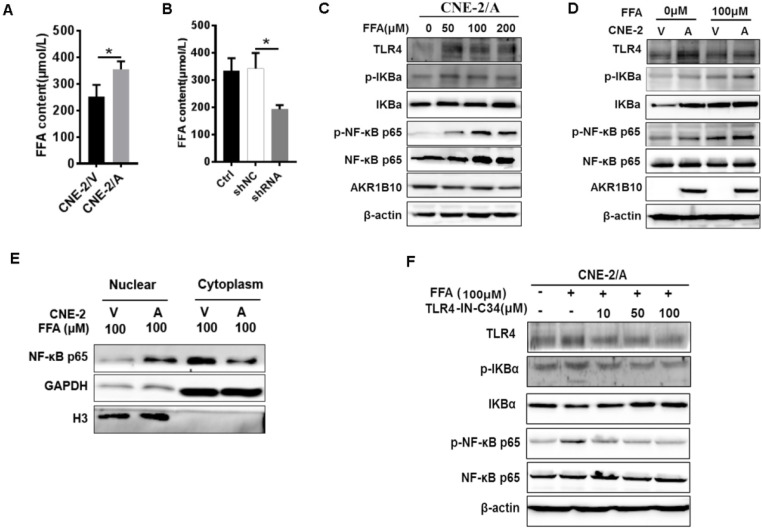
Figure 5.
Enhanced AKR1B10 expression activates the TLR4/ NF-κB signaling pathway. (A and B) The effect of AKR1B10 expression on FFA content. AKR1B10 expression increases FFA content of CNE-2/AKR1B10 cells (CNE-2/A), meanwhile, knockdown of AKR1B10 expression decreases FFA content. (C) 0, 50, 100 and 200 µM FFA were used to treat CNE-2/AKR1B10 cells and the expression levels of TLR4, p-IKBɑ and p-NF-κB p65 as well as AKR1B10 were detected by western blot. (D) The expression levels of TLR4, p-IKBɑ and p-NF-κB p65 as well as AKR1B10 were further confirmed in the CNE-2/vector and CN-2/AKR1B10 cells after treated with 100 μM FFA. (E) The effect of FFA on NF-κB p65 entry into the nucleus. (F) The effect of FFA inhibitors on TLR4 signaling pathway. A: AKR1B10; V: vector, psin-EF2-puromycin; CNE-2/A: CNE-2/AKR1B10, AKR1B10 expressed CNE-2 cells; CNE-2/V: CNE-2/AKR1B10 vector, CNE-2 control cells; FFA: Free fatty acid; H3: H3 histone; TLR4-IN-C34:TLR4 inhibitor; p-IKBɑ: phosphorylated IKBα; p-NF-κB: phosphorylated NF-κB. *P < 0.05.