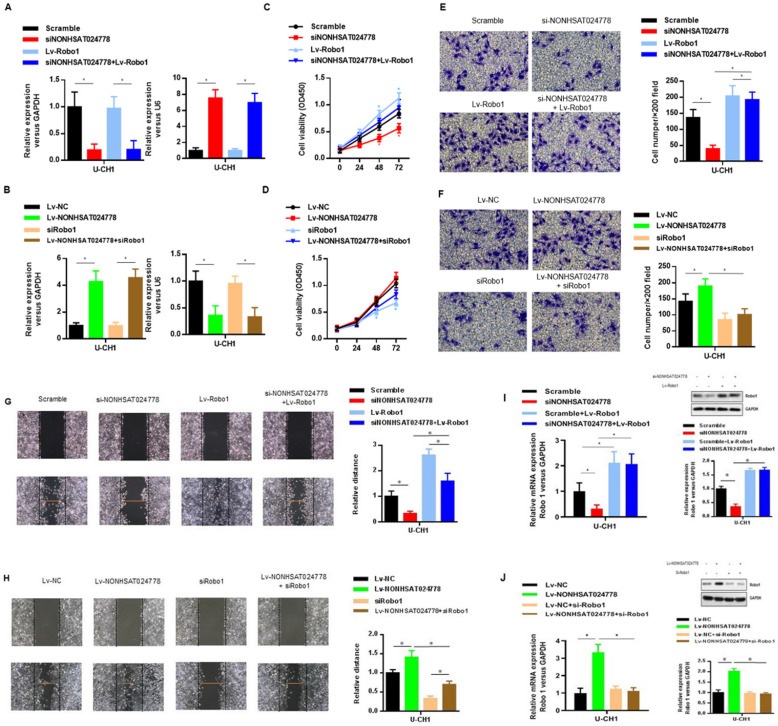
Figure 6.
The effects of Robo1 on chordoma cells viability in vitro (*P<0.05). (A, B) qRT-PCR was used to measure mRNA level. Left, The NONHSAT024778 mRNA level of si-NONHSAT024778+ Lv-Robo1 or Lv-NONHSAT024778+si-Robo1 transfected U-CH1 cell in parallel with control vector. Right, The miR-1290 mRNA level of si-NONHSAT024778+Lv-Robo1 or Lv-NONHSAT024778+si-Robo1 transfected U-CH1 cell in parallel with control vector. (C, D) U-CH1 cell growth after transfection with si-NONHSAT024778+Lv-Robo1 or Lv-NONHSAT024778+si-Robo1 or control vector was determined by CCK8. (E, F) Transwell assays were used to investigate the changes in invasive ability of chordoma cells transfected with si-NONHSAT024778+Lv-Robo1 or Lv-NONHSAT024778+si-Robo1 or control vector. (G, H) Migration ability of U-CH1 cells after transfection with si-NONHSAT024778+Lv-Robo1, Lv-NONHSAT024778+si-Robo1 or control vector was determined by wound healing assay. (I, J) The mRNA and protein expression of Robo1 was measured in U-CH1 cells transfected with si-NONHSAT024778+Lv-Robo1, Lv-NONHSAT024778+si-Robo1 or control vector.