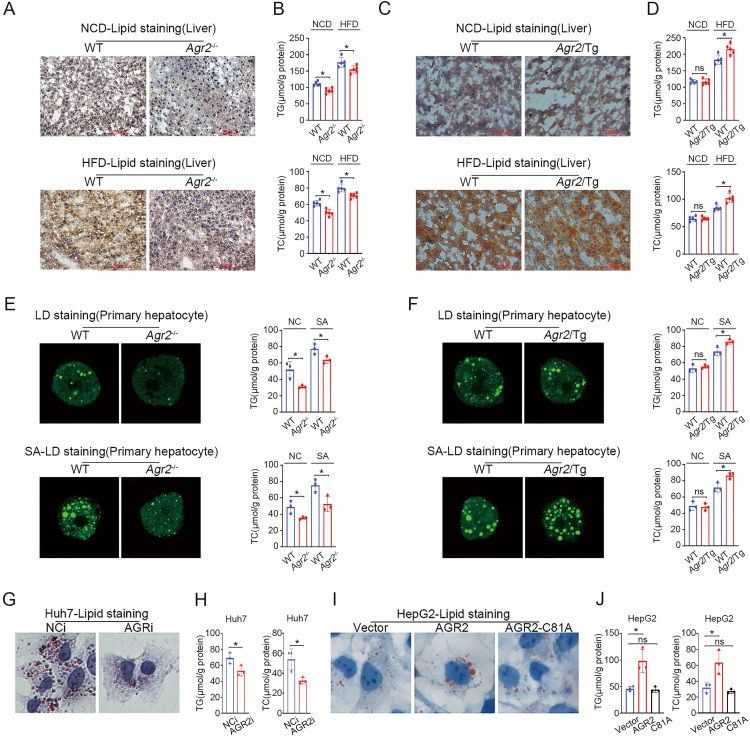
Figure 2.
AGR2 promotes hepatic lipid synthesis. The 8-week-old mice were fed a NCD or a HFD for an additional 10 weeks. A. Lipid staining in liver tissue from WT and Agr2-/- mice fed a NCD (top) or a HFD (bottom). B. TG (top) and TC (bottom) contents in the livers of WT and Agr2-/- mice fed a NCD or a HFD (n=5). C. Lipid staining in liver tissue from WT and Agr2/Tg mice fed a NCD (top) or a HFD (bottom). D. TG (top) and TC (bottom) contents in the livers of WT and Agr2/Tg mice fed a NCD or a HFD (n=5). E. Lipid droplet staining (left) and TG and TC contents (right) in primary hepatocytes in WT and Agr2-/- mice under normal conditions or under exposure to stearic acid. F. Lipid droplet staining (left) and TG and TC (right) in primary hepatocytes in WT and Agr2/Tg mice under normal conditions or under exposure to stearic acid. G. Lipid staining in Huh7 cells treated with siRNA targeting AGR2. H. TG and TC contents in Huh7 cells treated with siRNA targeting AGR2. I. Lipid staining in HepG2 cells treated with AGR2 and AGR2-C81A expression plasmids. J. TG and TC contents in HepG2 cells treated with AGR2 and AGR2-C81A expression plasmids. Representative figures were generated with data from at least three independent experiments. The data are presented as the mean ± SD values. *P < 0.05 by Student's t test.