Fig. 3.
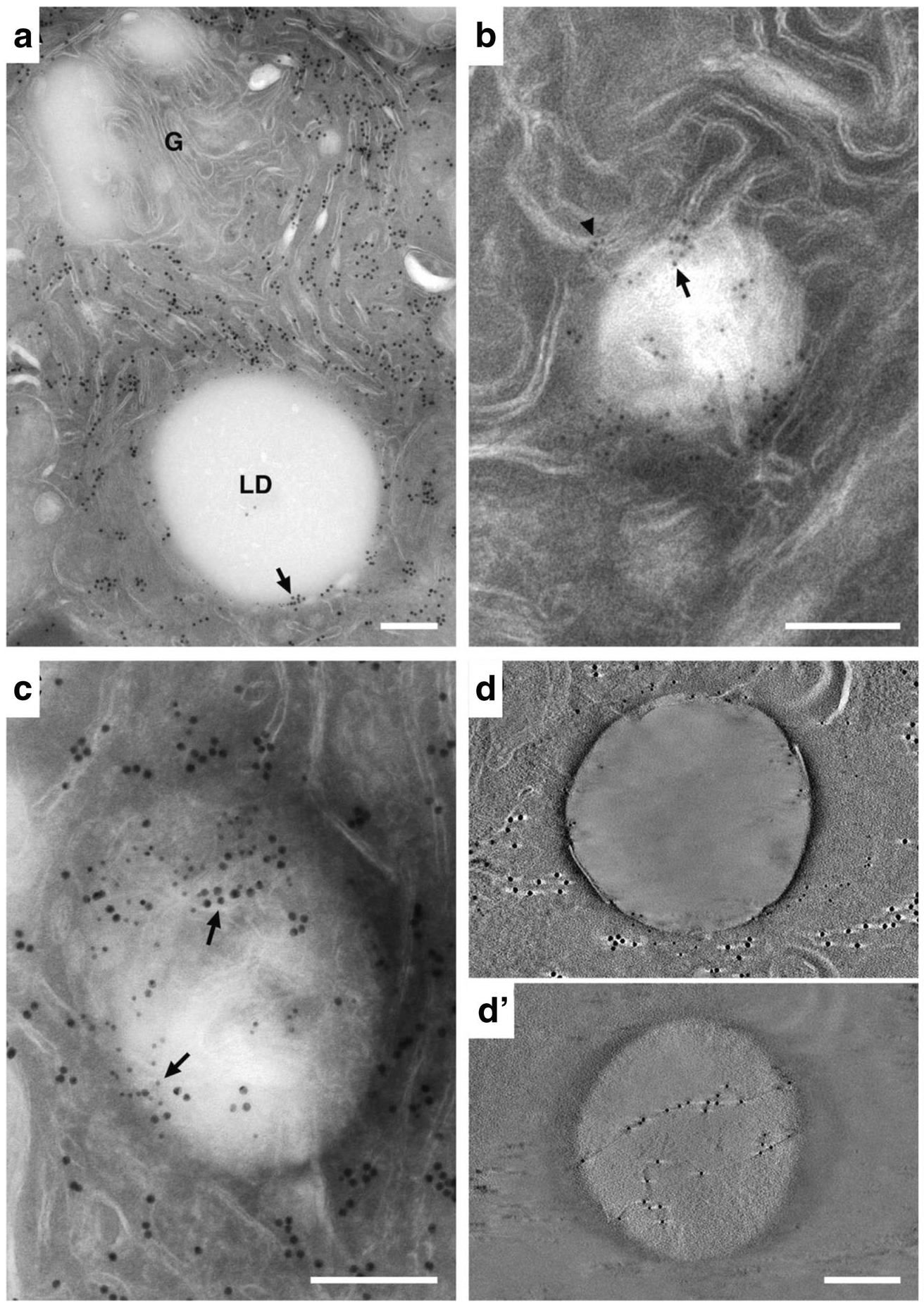
Immuno-EM localization of ER and lipid droplet markers in lactating mammary epithelial cells. (A) Double-labeled section showing the localization of PDI (15 nm gold) and Plin2 (10 nm gold). Abundant PDI is detected on ER throughout the section but is not present on the Golgi complex (G). Plin2 selectively localizes to the LD surface. PDI and Plin2 co-localize at distinct places on the surface of the LD (arrow). The inset is an enlargement of the boxed area showing 10 nm gold labelled Plin2 localizing to the LD surface (arrow) and 15 nm gold labelled PDI localizing to the ER (arrowhead). (B) Detail of a lipid droplet in a thin (100 nm) section labeled with antibodies against Plin2. Gold is localized to membranes at the periphery of the droplet (arrowhead), some of which appear to penetrate into the body of the droplet (arrow). (C) Double-labeled 100 nm section showing PDI (15 nm gold, small arrows) and Plin2 (10 nm gold, large arrows) colocalizing at the periphery and within the body of the LD (arrows). (D & D’) Tomographic reconstructions of thin sections labeled with antibodies to PDI and Plin2. (D) A 0.91 nm tomographic slice from the surface of the reconstruction showing Plin2 on the LD surface and PDI near the droplet periphery (the light streaks extending from either side of the large gold particles are artifacts of single axis tomographic reconstruction [38]). (D’) A 0.91 nm tomographic slice from within the LD interior demonstrating that Plin2 labels strands that cross through the interior of the droplet. Bars = 0.2 μm
