Fig 6.
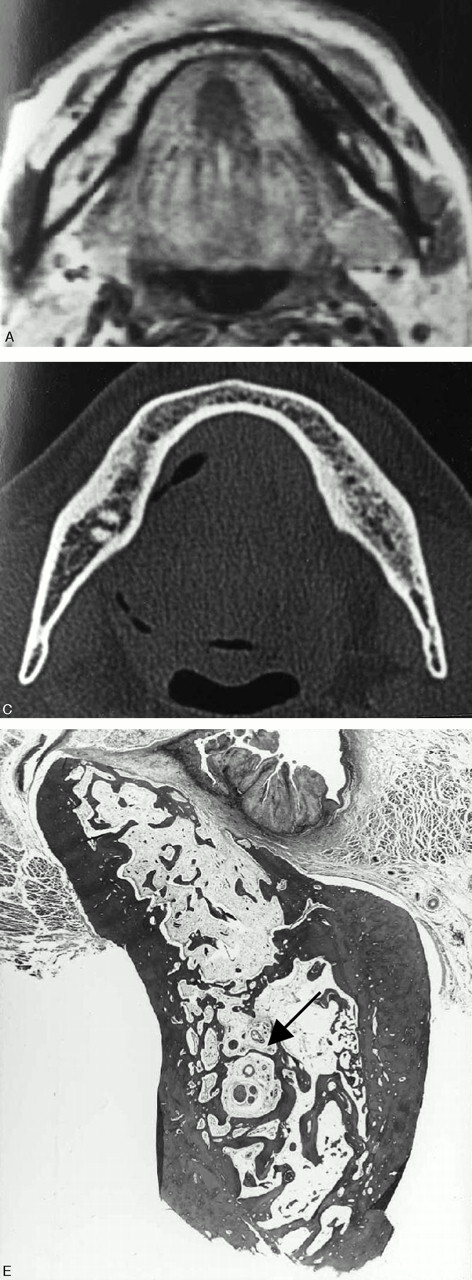
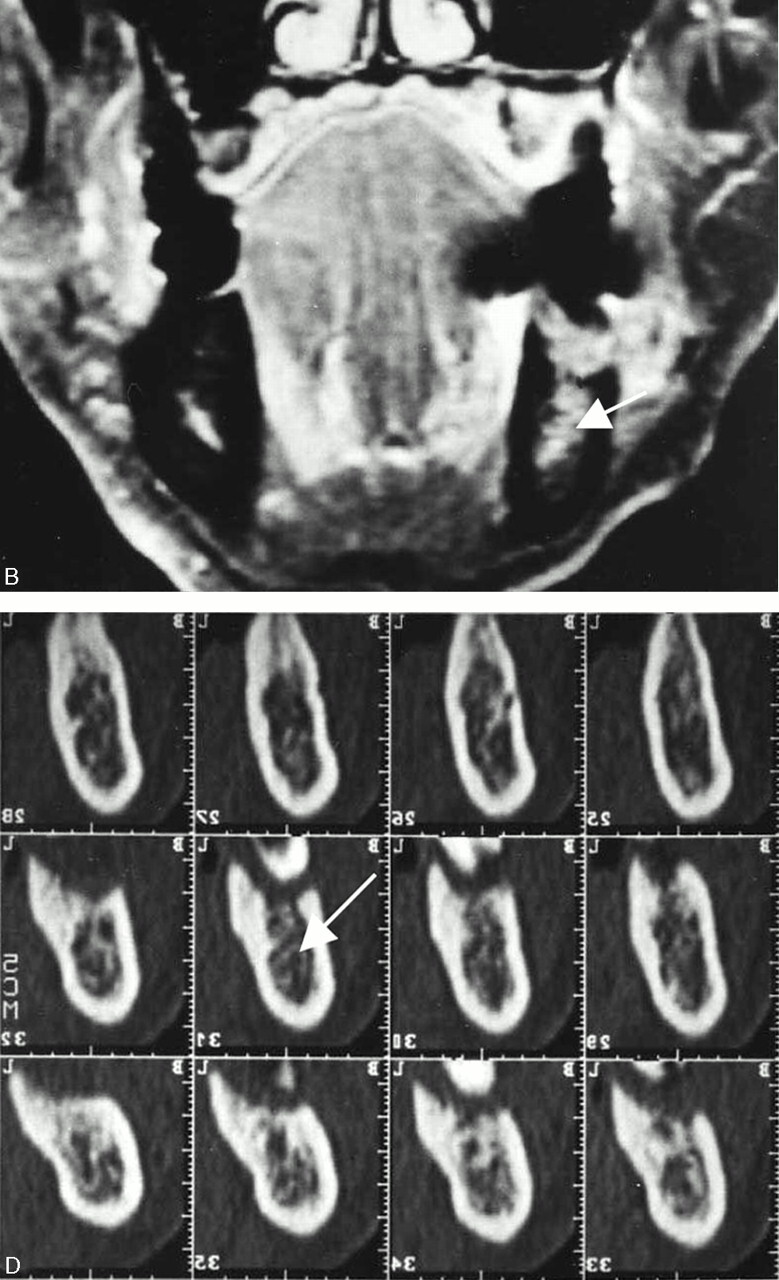
A 69-year-old man with left lower gingival carcinoma showing a false-positive result with MR imaging and true-negative result with CT for the involvement of inferior alveolar canal.
A, Axial T1-weighted image (560/14).
B, Contrast-enhanced coronal T1-weighted image (520/14).
C, Axial bone algorithm CT image.
D, Dental CT reformatted images.
E, Photomicrograph of the surgical specimen (Hematoxylin and eosin stain; original magnification, ×5.3)
MR images reveal abnormal signal intensity of bone marrow in the left molar region reaching the inferior alveolar canal (B, arrow), suggestive of inferior alveolar canal involvement. However, no involvement of the canal (D, arrow) is suspected on CT images. The photomicrograph of the surgical specimen reveals tumor invasion into the bone marrow with small focal alveolar bone absorption. Reactive fibrous change spreads in the bone marrow and reaches the inferior alveolar canal (E, arrow), which accounts for the overestimating of tumor extent with MR imaging.
