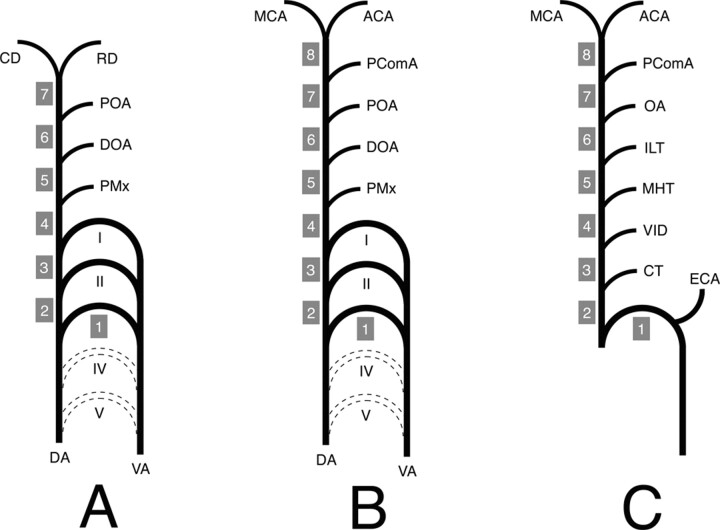
Fig 3.
Schematic representation of the ICA developmental anatomy.
I, II, III, IV, and V, aortic arch I–V; ACA, anterior cerebral artery; CD, caudal division of the ICA; CT, caroticotympanic artery; DA, dorsal aorta; DOA, dorsal ophthalmic artery; ECA, external carotid artery; ILT, inferolateral trunk; MCA, middle cerebral artery; MHT, meningohypophyseal trunk; OA, ophthalmic artery; PComA, posterior communicating artery; POA, primitive ophthalmic artery; PMx, primitive maxillary artery; RD, rostral division of the ICA; VA, ventral aorta; VID, vidian artery.
A, ICA embryology according to Lasjaunias and Santoyo-Vazquez (1). The ICA is constituted of seven segments separated by embryonic vessels. Segment 1 is derived for the third aortic arch, whereas all the other segments (2–7) come from the DA. The distal ICA bifurcates into the RD and CD.
B, Modified ICA embryology. A new segment (8) has been added owing to reported observation. The PComA is now considered as an embryonic branch separating two segments (7 and 8) and no longer as the CD of the ICA. The ICA termination corresponds to its bifurcation into the ACA and MCA.
C, Schematic representation of the adult ICA based on the developmental anatomy described above. The ICA is derived from eight embryologic segments. The segment labeling (1–8) corresponds to the labeling in Figure 1.