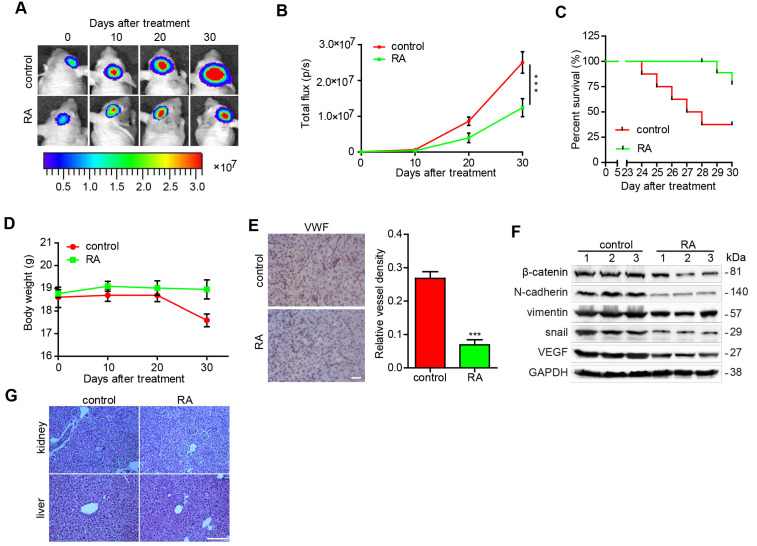
Figure 4.
RA decreased glioma growth in an orthotopic xenograft mouse model U87-luciferace cells (5×105) were intracranially injected into the mid-right striatum of 6-weeks-old male BALB/c nude mice. 5 days after injection, tumor formation was examined using bioluminescence imaging and the mice were divided into two groups: mice that were intraperitoneally injected with the vehicle (control) and mice that were intraperitoneally injected with RA (100 mg/kg/day). Tumor sizes were measured once every 10 days. Bioluminescence imaging was used to measure tumor volume. (A) The tumor volume of mice in each group determined at each time point (B) Tumor volume of mice in each group determined at each time point (C) The survival rate of mice in each group (D) The body weight of the mice was measured at the time points indicated. At the end of the experiment or after the mice had died, their brains were collected. (E) VWF (Bar, 50 μm) were used to stain the mice brains. Images of the brain were captured and analyzed using Image Pro-Plus software. (F) At the end of the experiment or after the mice had died, tumor tissues were collected from the mice and the protein lysates obtained were examined to determine levels of protein expression. (G) the kidney and liver tissues were obtained and HE-stained (Bar, 500μm). ***, P < 0.001, compared with the control.